My gaming PC lags in new titles. How can I optimize settings for better FPS?

Understanding the Performance Challenge
As new game titles push the boundaries of graphical fidelity and complex simulations, even well-specced gaming PCs can start to show their age or struggle under the load. Experiencing lag, stuttering, or consistently low frame rates per second (FPS) can ruin an otherwise immersive experience. The good news is that often, significant improvements can be made through intelligent optimization of both in-game graphics settings and your system configuration.
In-Game Graphics Settings: Your First Line of Defense
The most direct way to boost FPS is by adjusting the settings within the game itself. Modern titles offer a plethora of options, each impacting performance differently.
Resolution: The Biggest FPS Gainer
Lowering your game’s resolution is arguably the most impactful change you can make for FPS. Rendering fewer pixels significantly reduces the workload on your graphics card. While native resolution (e.g., 1080p, 1440p) provides the sharpest image, dropping one step down (e.g., from 1440p to 1080p) or even using a resolution scaling feature can yield massive frame rate increases at the cost of a slightly less crisp image.

Graphics Quality Presets vs. Individual Settings
Most games offer general graphics presets like ‘Low,’ ‘Medium,’ ‘High,’ or ‘Ultra.’ Starting with a lower preset (e.g., Medium) can be a good baseline, then you can fine-tune individual settings. Here are some key settings to prioritize lowering if you’re chasing higher FPS:
- Texture Quality: This impacts how detailed surfaces look. Lowering it can free up VRAM, especially if your GPU has less than 8GB.
- Shadow Quality: Shadows are notoriously demanding on both CPU and GPU. Reducing their quality or even disabling complex shadows can provide a noticeable FPS boost.
- Anti-Aliasing (AA): This setting smooths jagged edges. Techniques like MSAA are very demanding, while FXAA or TAA are less so. Experiment with lower settings or turn it off entirely if performance is critical.
- Ray Tracing: While visually stunning, ray tracing is incredibly demanding. If your FPS is struggling, this is often the first setting to disable.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO): This adds realistic shading where surfaces meet. Lowering or disabling it can offer a small but worthwhile performance gain.
- Post-Processing Effects: Bloom, depth of field, motion blur, and lens flare can add atmosphere but also consume resources. Turn them off if you don’t mind the aesthetic change.
- Draw Distance / Level of Detail (LOD): Reducing how far objects are rendered or their detail level at a distance can improve both CPU and GPU performance.

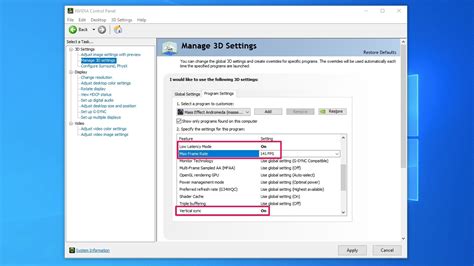
V-Sync and Frame Rate Caps
V-Sync synchronizes your game’s frame rate with your monitor’s refresh rate to prevent screen tearing. While it can offer a smoother visual experience, it can also introduce input lag or cap your FPS unnecessarily if your hardware can achieve higher frame rates. Try disabling V-Sync or using adaptive sync technologies (G-Sync/FreeSync) if your monitor supports them. Additionally, some games allow you to set a maximum FPS. Capping your FPS slightly below your average can reduce fluctuations and provide a more stable experience.
System-Level Optimizations for Peak Performance
Beyond in-game settings, optimizing your operating system and drivers can significantly improve your gaming performance.
Keep Your Drivers Updated
Graphics card drivers (NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) are critical for performance. Manufacturers frequently release new drivers optimized for the latest game titles. Always ensure you’re running the most up-to-date drivers for your GPU. Don’t forget chipset drivers and other essential system drivers from your motherboard manufacturer as well.

Minimize Background Processes
Other applications running in the background can consume valuable CPU, RAM, and GPU resources. Before launching a demanding game, close unnecessary programs like web browsers, streaming apps, cloud storage clients, and other non-essential software. Windows Game Mode can also help by prioritizing game processes.
Power Plan and Other Windows Settings
Ensure your Windows power plan is set to ‘High Performance’ or ‘Ultimate Performance’ to prevent your CPU from throttling. Additionally, consider disabling some visual effects in Windows (e.g., animations, shadows under windows) via the ‘Adjust the appearance and performance of Windows’ setting in the Control Panel.

Monitor and Analyze Your Performance
Tools like MSI Afterburner (with RivaTuner Statistics Server) or the Xbox Game Bar’s performance overlay can help you monitor your CPU, GPU, RAM usage, and FPS in real-time. This data is invaluable for identifying bottlenecks. If your GPU usage is consistently at 99-100% while your CPU usage is low, you’re GPU-bound, and reducing graphical settings will help. If your CPU is maxed out and GPU usage is low, you’re CPU-bound, and you might need to adjust settings that affect CPU load (like draw distance, crowd density, or physics).
When All Else Fails: Hardware Considerations
If you’ve optimized everything and still can’t achieve satisfactory FPS, your hardware might genuinely be struggling to meet the demands of truly cutting-edge titles. In such cases, upgrading components like your graphics card, CPU, or adding more RAM might be the ultimate solution. However, always exhaust all software optimization options first, as they are free and often highly effective.

Finding Your Sweet Spot
Optimizing for better FPS is a balancing act between visual fidelity and performance. Start with the most impactful changes (resolution, shadows, anti-aliasing) and gradually tweak other settings until you find a ‘sweet spot’ that offers both enjoyable visuals and smooth frame rates. Don’t be afraid to experiment; every system and game is different, and what works best for one might not be ideal for another. Happy gaming!