How do I troubleshoot conflicting game mods for stable gameplay?
Modding a game can transform it into an entirely new experience, adding new features, improving graphics, and extending its lifespan. However, the more mods you install, the higher the chance of encountering conflicts that lead to crashes, bugs, or unstable gameplay. Don’t let these frustrations deter you; troubleshooting mod conflicts is a skill that can be learned, ensuring your modded adventures remain enjoyable and consistent.
Understanding Mod Conflicts
Game mod conflicts arise when two or more mods attempt to modify the same game file, script, or resource in incompatible ways. This can manifest in various forms:
- File Overwrites: One mod replaces files critical to another.
- Load Order Issues: Mods load in an incorrect sequence, causing expected changes to be overridden or not applied.
- Scripting Discrepancies: Mods try to execute conflicting commands or rely on different versions of the same script.
- Feature Incompatibilities: Two mods introduce features that are inherently designed to work differently or cannot coexist.

Preparation: The Foundation of Stable Modding
Before diving into troubleshooting, robust preparation can save you hours of headaches.
1. Use a Mod Manager
Tools like Vortex, Mod Organizer 2, or Nexus Mod Manager are indispensable. They handle installation, uninstallation, and often detect basic conflicts. Crucially, they manage your mod load order and allow for virtual installations, keeping your game’s data folder clean.
2. Back Up Your Game and Saves
Always back up your vanilla game directory before installing any mods. Similarly, regularly back up your save files. This ensures you can revert to a stable state if something goes catastrophically wrong.
3. Read Mod Descriptions Thoroughly
Many mod authors list known incompatibilities, required patches, or specific installation instructions. Ignoring these is a common cause of conflicts.
The 50/50 Method: Isolating the Culprit
This systematic approach is one of the most effective ways to find a conflicting mod, especially when you have a large mod list.
- Start with a Crash: Identify the specific issue (e.g., game crashes on startup, specific quest bug).
- Disable Half Your Mods: If your game crashes with all mods enabled, disable approximately half of them.
- Test the Game:
- If the crash persists, the conflicting mod is in the enabled half.
- If the crash stops, the conflicting mod is in the disabled half.
- Repeat and Refine: Take the problematic half and disable half of those mods. Continue this process, narrowing down the suspected mods until you isolate the single (or few) mods causing the issue.
This binary search method significantly reduces the number of tests required compared to disabling mods one by one.
Advanced Tools and Techniques
For more complex conflicts, especially in games like Skyrim or Fallout, dedicated tools are invaluable.
1. Load Order Optimizers
Tools like LOOT (Load Order Optimisation Tool) automatically sort your mod plugins into an optimal load order based on community-sourced rules. While not a magic bullet, it resolves many common load order conflicts.
2. Conflict Resolution Patches (CRPs)
Some communities create dedicated patches to make incompatible mods work together. Search for these on modding websites. Alternatively, tools like xEdit (FO4Edit, SSEEdit, FNVEdit, etc.) allow you to create your own patches by manually resolving record conflicts. This involves opening two conflicting mods and deciding which mod’s changes you want to prioritize for specific game records.
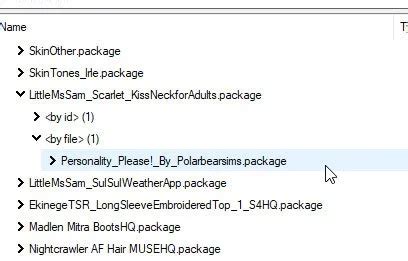
3. Reading Crash Logs
Many games or modding frameworks generate crash logs. These logs often contain clues about the last files or scripts accessed before a crash, pointing directly to the problematic mod or resource.
Common Conflict Scenarios & Solutions
Texture & Mesh Conflicts
Often, these are less critical and simply result in one mod’s assets being overwritten by another. Use your mod manager’s file conflict resolution features (usually prioritizing one over the other) or install the desired texture/mesh last.
Script Conflicts
These are more serious and frequently lead to crashes or broken quests. They often require specific compatibility patches or manual merging via tools like xEdit. If no patch exists, you might have to choose between the conflicting mods.
UI/HUD Conflicts
Multiple UI mods can overwrite each other’s files, leading to missing interface elements or graphical glitches. Ensure only one major UI overhaul is active, and use compatible add-ons designed to work with it.
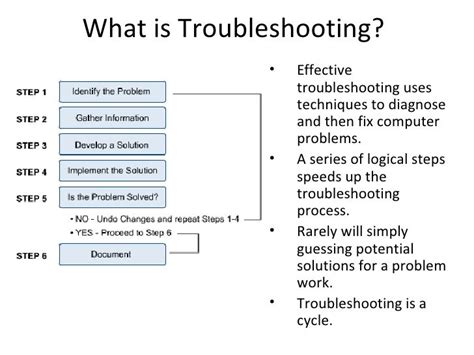
Prevention and Best Practices
- Install Mods Incrementally: Don’t install 50 mods at once. Add a few, test thoroughly, then add more.
- Test Frequently: After adding or removing mods, play the game for a while to ensure stability.
- Keep Mods Updated: Mod authors often release updates with bug fixes and compatibility improvements.
- Engage with the Community: Modding forums, Discord servers, and the comment sections on mod pages are invaluable resources for help and known issues.

Conclusion
Troubleshooting conflicting game mods can be a daunting task, but with a systematic approach, the right tools, and a bit of patience, you can transform your unstable game into a seamless modded masterpiece. Embrace the challenge, learn from each conflict, and enjoy the rich, personalized gaming experience that modding offers.







