Optimize gaming PC performance: What BIOS settings boost FPS?

Unlock Your Gaming PC’s Full Potential Through BIOS
Many gamers focus on upgrading their GPU or CPU to squeeze out more frames per second (FPS). While hardware upgrades are crucial, a often-overlooked avenue for performance gains lies within your motherboard’s Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). Properly configured BIOS settings can significantly impact your PC’s gaming performance, leading to smoother gameplay and higher FPS without spending an extra dime on new components. This guide will walk you through the essential BIOS settings that can give your gaming rig the edge it needs.
Before diving in, remember that modifying BIOS settings carries risks. Incorrect changes can lead to system instability, boot failures, or even hardware damage. Always proceed with caution, understand each setting’s purpose, and consult your motherboard manual if unsure. It’s highly recommended to backup your current BIOS settings if your motherboard supports it, and to only change one setting at a time so you can easily identify the cause of any issues.
Key BIOS Settings to Boost Gaming FPS
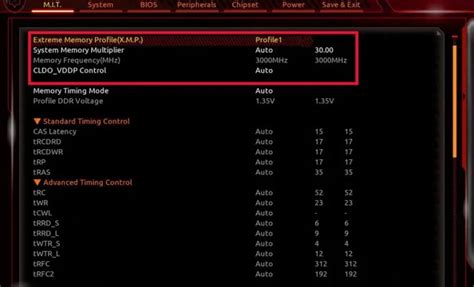
1. Enable XMP/DOCP (Extreme Memory Profile / Direct Overclock Profile)
One of the most impactful settings for gaming performance is ensuring your RAM runs at its advertised speed. Out of the box, your RAM often defaults to a lower JEDEC standard speed (e.g., 2133MHz or 2400MHz), even if it’s rated for much faster speeds (e.g., 3200MHz or 3600MHz). XMP (Intel) or DOCP (AMD) profiles are pre-configured settings that tell your motherboard to run your RAM at its optimal speed and timings.
How it helps: Faster RAM reduces latency and increases bandwidth, which directly translates to better CPU performance in memory-intensive tasks, including gaming, resulting in a noticeable FPS boost, especially in CPU-bound scenarios.
2. Resizable BAR / Smart Access Memory (SAM)
Resizable BAR (PCIe Resizable Base Address Register) and AMD’s Smart Access Memory (SAM) are technologies that allow your CPU to access your GPU’s entire VRAM directly, rather than in small 256MB chunks. This can significantly improve performance in many modern games by reducing bottlenecks and improving data transfer efficiency.
How it helps: Depending on the game and hardware combination, enabling Resizable BAR/SAM can offer anywhere from a modest 5% to a substantial 15% FPS increase. You’ll need a compatible CPU (Intel 10th Gen+ or AMD Ryzen 3000 series+) and GPU (Nvidia RTX 30/40 series or AMD RX 6000/7000 series+), along with a compatible motherboard and a UEFI BIOS.
3. CPU Overclocking (Proceed with Extreme Caution)
For advanced users, manual CPU overclocking can yield significant performance gains. This involves increasing the CPU’s clock speed beyond its factory settings. Most modern CPUs offer some form of overclocking, either through a simple multiplier adjustment or more complex voltage and frequency tuning.
How it helps: A faster CPU can process game logic, AI, and physics more quickly, feeding the GPU with frames at a higher rate. This is particularly beneficial in CPU-intensive games or scenarios where your GPU isn’t fully utilized. However, overclocking requires proper cooling and careful stability testing, as it increases power consumption and heat generation. Start with small increments and monitor temperatures closely.

4. Disable Virtualization Technology (VT-x / AMD-V)
Most modern CPUs include virtualization technologies (Intel VT-x or AMD-V) that allow a single physical CPU to be split into multiple virtual CPUs, essential for running virtual machines. If you don’t use virtual machines, hypervisors, or Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), disabling this feature can sometimes free up system resources.
How it helps: While the performance impact is often minimal for pure gaming, disabling virtualization ensures that no overhead is created by processes that might utilize this feature in the background, potentially offering a fractional gain or increased stability.
5. Power Management Settings
Many motherboards have various power management settings. Ensure that your CPU is set to operate at its full potential when under load. Look for settings like “CPU Power Management,” “Intel SpeedStep,” “AMD Cool’n’Quiet,” or “C-States.”
How it helps: While these technologies are great for power saving, they can sometimes introduce slight latency or prevent your CPU from immediately boosting to its maximum frequency when a sudden demand arises. Disabling aggressive power-saving features can ensure consistent high performance, although at the cost of higher power consumption and heat.
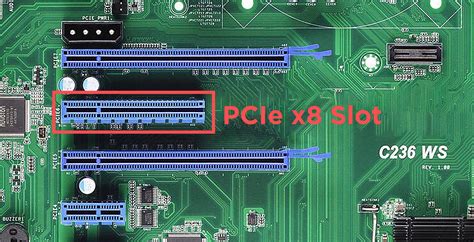
6. PCIe Link Speed
Check your PCIe Link Speed setting for your dedicated graphics card slot. Ensure it’s set to the highest generation supported by your motherboard and GPU (e.g., Gen3 or Gen4). While many games don’t saturate a Gen3 x16 slot, ensuring it’s running at its maximum potential eliminates any potential bottlenecks.
How it helps: This ensures your graphics card has the maximum available bandwidth to communicate with the CPU, which is crucial for high-resolution gaming and data-intensive applications. For modern GPUs and motherboards, setting this to Gen4 or even Gen5 is optimal.
7. Disable Integrated Graphics
If your CPU has integrated graphics (e.g., Intel UHD Graphics, AMD Radeon Graphics) and you are using a dedicated graphics card, it’s often best to disable the integrated graphics from the BIOS. Sometimes, the system might allocate a small amount of system RAM to the integrated GPU even if it’s not being used.
How it helps: Disabling integrated graphics ensures that all system resources, including RAM and CPU cycles, are fully dedicated to your dedicated GPU and the main system processes, preventing any potential conflicts or unnecessary resource allocation.

General Tips and Warnings
- Read Your Manual: Your motherboard’s manual is an invaluable resource. It details every BIOS setting specific to your board.
- Update Your BIOS: Sometimes, a BIOS update can introduce new features (like Resizable BAR support) or improve stability and compatibility. Always follow your manufacturer’s update instructions carefully.
- CMOS Clear: If you make a mistake and your system won’t boot, you can usually reset your BIOS to default settings by clearing the CMOS. Consult your motherboard manual for the specific procedure (usually involves a jumper or removing the CMOS battery).
- Monitor Temperatures: After any changes, especially overclocking, monitor your CPU and GPU temperatures under load using tools like HWMonitor or MSI Afterburner to ensure stability and prevent thermal throttling.

Conclusion
Optimizing your gaming PC isn’t just about raw hardware power; it’s also about intelligently configuring your system. By carefully adjusting these BIOS settings, you can unlock hidden performance potential, achieve higher FPS, and enjoy a smoother, more responsive gaming experience. Always remember to proceed with caution and understand the implications of each change to ensure system stability. A few minutes in your BIOS can translate into significant gains in your favorite games.









