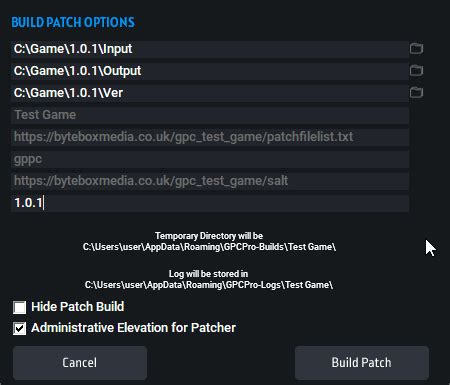
How can we best structure gaming guides for scannability and quick content updates?

The Challenge of Modern Gaming Guides
In the fast-paced world of gaming, players need information quickly and efficiently. A poorly structured guide can lead to frustration, while an outdated one quickly loses its value. Therefore, designing gaming guides for optimal scannability and ease of content updates is paramount for both player satisfaction and content creator efficiency.
Prioritizing Scannability for Gamers
Scannability ensures that users can rapidly locate the specific information they need without reading through dense blocks of text. This is crucial for guides covering complex game mechanics, build orders, quest walkthroughs, or item locations. Effective scannability hinges on clear visual hierarchy and concise information delivery.
Key Elements for Scannable Guides:
- Clear Headings and Subheadings: Use
<h2>,<h3>, and even<h4>tags to break down content into logical, digestible sections. Headings should be descriptive and direct. - Bullet Points and Numbered Lists: Ideal for presenting item lists, steps in a sequence, pros/cons, or ability descriptions. They offer immediate visual breaks and highlight key pieces of information.
- Short Paragraphs: Avoid lengthy paragraphs. Break information into smaller chunks, typically 2-4 sentences, to prevent reader fatigue.
- Bold Text and Callouts: Use bolding sparingly to emphasize critical keywords, names, or values. Special ‘Note’ or ‘Tip’ boxes can draw attention to important advice.

Strategic Use of Visuals and Layout:
Beyond text formatting, the overall layout contributes significantly to scannability. Employ generous white space to prevent pages from feeling cluttered. Consider using icons or small graphics to visually represent categories, items, or status effects, making information instantly recognizable.
- Tables: Essential for presenting comparative data, such as item stats, character abilities, or enemy weaknesses, in an organized, easy-to-read format.
- In-Guide Navigation: A sticky table of contents or anchor links within a long guide allows users to jump directly to relevant sections, saving time and improving usability.
Designing for Quick Content Updates
Games evolve, and so must their guides. Patches, expansions, and balance changes necessitate regular updates. Structuring guides with future updates in mind can drastically reduce maintenance time and ensure your content remains accurate and valuable.
Modular Content and Templates:
The core principle here is to treat information as modular blocks rather than monolithic texts. This means:
- Standardized Templates: Develop consistent templates for different guide types (e.g., character builds, quest guides, item databases). This ensures uniformity and makes it easier to update specific data points within a predictable structure.
- Atomic Information Units: Break down content into the smallest practical units. For instance, instead of describing an item’s stats within a paragraph, use a dedicated data block or table that can be easily updated if the item changes.
- Centralized Data Sources: For complex guides with many interconnected data points (e.g., skill trees, item inventories), consider if a backend database or structured data format (like JSON or YAML) could feed your guide content. This allows for global changes from a single source.

Version Control and Change Logs:
Transparency about updates builds trust with your audience.
- Clear Versioning: Indicate the game version or patch number the guide is relevant to.
- Update Logs: Include a small section or link to a change log detailing what has been updated, when, and why. This helps returning users quickly identify new information.
Practical Implementation Strategies
Combining scannability and update-friendliness requires a holistic approach to guide design and maintenance.
Leveraging SEO and Internal Linking:
While not strictly structural, thoughtful internal linking helps users (and search engines) navigate your content. Link to related guides, individual item pages, or specific sections within the same guide. Use descriptive anchor text.

Interactive Elements (Where Applicable):
For some platforms, interactive elements can enhance both scannability and update efficiency:
- Search Functionality: If your guide is part of a larger knowledge base, a robust search bar is invaluable.
- Hover-over Tooltips: Displaying detailed stats or descriptions on hover for complex terms or items can keep the main guide clean and scannable, while detailed data is easily accessible. Updates to these tooltips can be managed centrally.
Conclusion
Structuring gaming guides for scannability and quick content updates is not merely a nicety—it’s a necessity for relevance and user satisfaction. By adopting principles of clear visual hierarchy, modular content design, and transparent update practices, content creators can build guides that stand the test of time, serving the dynamic needs of the gaming community effectively.