Why is my FPS low in new games? Is my CPU or GPU the bottleneck for 1440p gaming?
Understanding Low FPS in Modern Games at 1440p
As new games push the boundaries of graphical fidelity and complex simulations, maintaining high frame rates per second (FPS), especially at higher resolutions like 1440p, becomes increasingly challenging. A noticeable drop in FPS can transform an immersive gaming experience into a frustrating slideshow. The core question for many PC gamers then becomes: is my Central Processing Unit (CPU) or Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) the primary culprit?
Modern titles demand significant resources from both components. Your GPU is responsible for rendering the visual splendor, handling textures, shaders, and complex lighting. Meanwhile, your CPU manages game logic, artificial intelligence, physics calculations, draw calls (telling the GPU what to render), and overall system operations. A balanced system ensures both work in harmony, but when one component can’t keep pace, a bottleneck occurs, limiting the potential of the other and resulting in lower FPS than desired.
The CPU vs. GPU Bottleneck Explained
Identifying whether your CPU or GPU is the bottleneck is crucial for effective troubleshooting and potential upgrade planning. A bottleneck essentially means one component is preventing another from performing at its full potential.
The Role of the GPU in 1440p Gaming
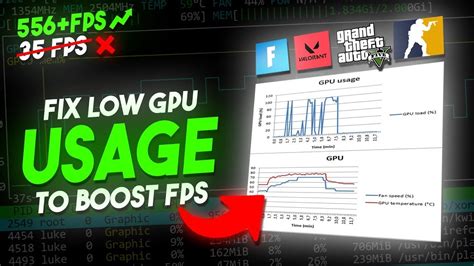
At 1440p, your GPU is under immense pressure. It has to render significantly more pixels than at 1080p (roughly 78% more, to be precise). High graphical settings, demanding anti-aliasing, and complex post-processing effects directly strain the GPU. If your GPU is consistently at 99-100% utilization while your CPU is relatively idle, it’s a strong indicator that your graphics card is the limiting factor.
The Role of the CPU in Gaming Performance
While often seen as less critical for resolution, a CPU’s role in gaming is vital. It prepares the frames for the GPU, handles game logic, AI, and physics. In CPU-intensive games, or scenarios with many on-screen characters and complex simulations (like large open-world games or strategy titles), a weaker CPU can struggle to feed frames to a powerful GPU fast enough, even if the GPU isn’t fully utilized.

How to Identify Your System’s Bottleneck
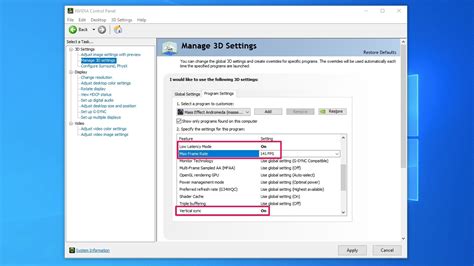
The most effective way to pinpoint a bottleneck is through real-time hardware monitoring while gaming. Several tools can help you track CPU and GPU utilization, temperatures, and clock speeds.
Monitoring Tools Are Your Best Friend
- MSI Afterburner (with RivaTuner Statistics Server): This widely used tool provides an in-game overlay displaying crucial statistics like GPU usage, CPU usage (per core), RAM usage, temperatures, and FPS.
- HWiNFO64: Offers comprehensive hardware information and sensor data, allowing for detailed logging and analysis.
- Task Manager (Windows): A quick way to see overall CPU and GPU usage, though less detailed than dedicated monitoring software.
Signs of a GPU Bottleneck
If you observe the following, your GPU is likely the bottleneck:
- GPU Usage at 99-100%: Your graphics card is working at its maximum capacity.
- CPU Usage is Low (e.g., 50% or less): Your CPU has more processing power to spare.
- Lowering Graphical Settings Significantly Boosts FPS: This indicates the GPU was struggling to render the complex visuals.
- Higher Resolution Reduces FPS More Dramatically: More pixels mean more work for the GPU.
Signs of a CPU Bottleneck
Your CPU might be the limiting factor if you notice:
- CPU Usage at 90-100% (especially on one or more cores): Your processor is struggling to keep up.
- GPU Usage is Low (e.g., 70% or less) with Fluctuating FPS: The GPU is waiting for the CPU to deliver frames.
- FPS Drops in CPU-intensive Areas: Games with many NPCs, complex physics, or large environments tend to stress the CPU.
- Lowering Resolution Has Little to No Impact on FPS: This suggests the CPU is limiting frame generation, not the GPU’s rendering power.

Factors Affecting 1440p Performance Beyond Bottlenecks
While CPU and GPU bottlenecks are common, other factors can contribute to low FPS:
Game Settings Optimization
Even with powerful hardware, certain in-game settings can be overly demanding. Experiment with settings like anti-aliasing, shadow quality, global illumination, and texture filtering. Often, a slight reduction in one or two settings can yield significant FPS gains with minimal visual impact.
Outdated or Corrupt Drivers
Always ensure your GPU drivers (NVIDIA GeForce Experience, AMD Radeon Software) are up-to-date. Outdated drivers can lead to performance issues and instability. Similarly, chipset drivers for your motherboard should also be current.

Cooling and Thermal Throttling
Overheating components (CPU or GPU) will automatically reduce their clock speeds to prevent damage, a process known as thermal throttling. This immediately impacts performance. Ensure your PC has adequate cooling, clean dust filters, and proper airflow.
Background Applications and Resource Hogs
Other programs running in the background (web browsers with many tabs, streaming software, antivirus scans) can consume valuable CPU, RAM, or GPU resources, leaving less for your game.
Troubleshooting Steps for Low FPS
Before considering upgrades, try these steps:
- Update All Drivers: GPU, chipset, and even BIOS if available.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring software to ensure CPU and GPU temperatures are within safe limits.
- Adjust In-Game Settings: Lower demanding settings (shadows, reflections, volumetric clouds, anti-aliasing) first.
- Close Background Applications: Free up system resources.
- Check Power Settings: Ensure your PC is set to ‘High Performance’ in Windows Power Options.
- Verify Game Files: Corrupt game files can sometimes cause performance issues.
- Clean Your PC: Remove dust from fans and heatsinks for better cooling.
When to Consider a Hardware Upgrade
If after all troubleshooting, your monitoring tools consistently show a bottleneck and you’re still not hitting your desired FPS at 1440p, it’s time to consider an upgrade. For a GPU bottleneck, upgrading to a more powerful graphics card is the clear path. For a CPU bottleneck, a newer, faster processor, often requiring a new motherboard and RAM, might be necessary. Aim for a balanced upgrade to avoid simply shifting the bottleneck from one component to another.

Conclusion
Low FPS in new 1440p games is a common challenge, but understanding the intricate relationship between your CPU and GPU is the first step toward a solution. By utilizing monitoring tools and systematically addressing potential issues, you can accurately identify whether your CPU, GPU, or another factor is holding back your gaming performance. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions, optimize your settings, and if necessary, plan a targeted hardware upgrade to get back to enjoying fluid, high-fidelity gaming.