How can I improve CPU/GPU cooling in my gaming PC for better performance?

The Critical Role of PC Cooling in Gaming Performance
For any serious gamer, maintaining optimal temperatures for their CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is paramount. Overheating components lead to a phenomenon known as thermal throttling, where your hardware automatically reduces its clock speed to prevent damage. This directly translates to reduced frame rates, stuttering, and an overall degraded gaming experience. Furthermore, consistently high temperatures can shorten the lifespan of your valuable components. Fortunately, there are several effective strategies you can employ to significantly improve your PC’s cooling performance.
Optimizing Case Airflow for Maximum Efficiency
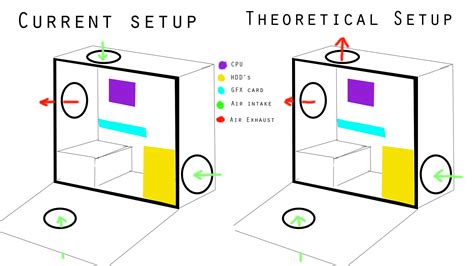
The foundation of effective cooling starts with proper airflow within your PC case. Think of your case as a wind tunnel; you want cool air to enter efficiently and hot air to exit quickly. Most modern cases are designed with airflow in mind, but user configuration is key.
Fan Placement and Configuration
- Intake Fans: Typically placed at the front or bottom of the case, these fans pull cool air into the system. Aim for slightly more intake than exhaust to create positive air pressure, which helps prevent dust ingress.
- Exhaust Fans: Usually located at the rear and top, these fans push hot air out of the case. Hot air rises, so top-mounted exhaust fans are particularly effective.
- Fan Speed: Utilize your motherboard’s fan control software or BIOS settings to create intelligent fan curves that increase speed under load and decrease it during idle periods, balancing performance with noise.
Cable Management and Dust Control
Messy cables can obstruct airflow, creating dead zones where hot air can accumulate. Take the time to route cables neatly behind the motherboard tray and out of the main airflow path. Additionally, dust is an insulator and can severely impede cooling. Regularly clean your case filters and components with compressed air. Many cases come with removable dust filters for easier maintenance.
Enhancing CPU Cooling Solutions
The CPU is often the heart of your gaming rig and can generate significant heat, especially during demanding games or overclocking. Upgrading its cooler is one of the most impactful improvements you can make.
Air Cooling vs. Liquid Cooling
- High-Performance Air Coolers: Large tower coolers with multiple heat pipes and powerful fans can rival liquid cooling in performance and are generally more affordable and less prone to failure. They are a robust and reliable choice.
- All-in-One (AIO) Liquid Coolers: These sealed units offer excellent cooling performance, often look sleeker, and can be easier to install than custom loops. They are particularly effective in smaller cases where large air coolers might not fit.
- Custom Liquid Cooling Loops: For enthusiasts seeking the ultimate in cooling performance and aesthetics, a custom loop allows for cooling multiple components (CPU, GPU, RAM, motherboard) with highly efficient radiators, pumps, and reservoirs. This option requires significant investment and expertise.
Thermal Paste Application
Regardless of your cooler type, proper application of thermal paste between the CPU’s Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) and the cooler’s cold plate is crucial. Old, dried-out thermal paste significantly reduces heat transfer. Reapply a fresh, high-quality thermal paste every few years or when you replace your cooler.

Boosting GPU Cooling Performance
The GPU is often the hottest component in a gaming PC, especially under heavy load. Ensuring it stays cool is vital for stable frame rates and longevity.
Aftermarket Coolers and Fan Curves
While most GPUs come with competent factory coolers, some models can run hot. Aftermarket GPU coolers (like those from Arctic Accelero) can drastically reduce temperatures, though they require careful installation and may void your warranty. For factory coolers, adjusting your GPU’s fan curve using software like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X1 allows you to make fans spin faster at lower temperatures, proactively managing heat before it becomes critical. Be mindful of noise levels when increasing fan speeds.
Repasting Your GPU
Just like with your CPU, the thermal paste on your GPU’s die can degrade over time. Replacing it with a fresh application of high-quality thermal paste can yield significant temperature drops, often 5-10°C or more. This is a more involved process than CPU repasting as it requires disassembling the GPU cooler, but it’s a worthwhile upgrade for older or hot-running cards.
General Maintenance and Environmental Factors
Beyond hardware upgrades, consistent maintenance and environmental awareness play a significant role in long-term cooling performance.
- Regular Cleaning: Periodically use compressed air to clear dust from all fans, heatsinks, and vents. A clean PC breathes better.
- Temperature Monitoring: Use software like HWMonitor, HWiNFO, or your GPU utility to keep an eye on CPU and GPU temperatures. Understand what normal operating temperatures are for your components (typically below 80°C under load is good, lower is better).
- Room Temperature: The ambient temperature of your room directly impacts your PC’s cooling capabilities. A cooler room means cooler intake air and thus cooler components.
- Proper PC Placement: Ensure your PC case has adequate clearance from walls or other obstructions to allow for unimpeded airflow. Don’t place it in an enclosed cabinet without proper ventilation.

Conclusion
Improving CPU and GPU cooling in your gaming PC is a multi-faceted endeavor that combines thoughtful hardware choices with diligent maintenance. By optimizing case airflow, upgrading your CPU cooler, fine-tuning GPU cooling, and adhering to regular cleaning schedules, you can ensure your system runs cooler, performs better, and lasts longer. Invest the time and effort into your cooling setup, and your gaming PC will reward you with a consistently smooth and powerful experience.









