How to boost FPS in AAA titles? GPU settings & driver tips needed.

Achieving high Frame Rates Per Second (FPS) in demanding AAA titles is crucial for a smooth, immersive, and competitive gaming experience. While upgrading your hardware is often the most straightforward path, there are numerous software-based optimizations you can implement to squeeze extra performance out of your existing graphics card and system. This guide will walk you through essential GPU settings and driver tips to boost your FPS in your favorite demanding games.
Driver Optimization: The Foundation of Performance
Your graphics card drivers are the bridge between your hardware and the games you play. Keeping them up-to-date and properly installed is arguably the most critical step in optimizing your gaming performance.
Keep Your Drivers Updated
NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel frequently release new driver versions that include performance optimizations for new game releases, bug fixes, and general improvements. Always ensure you’re running the latest stable driver version for your GPU. You can download these directly from the manufacturer’s website or use their respective software (NVIDIA GeForce Experience, AMD Adrenalin Software).
Perform a Clean Installation
When updating drivers, especially if you’re experiencing issues, consider performing a clean installation. This removes all previous driver files and settings, preventing potential conflicts or leftover junk. Both NVIDIA and AMD driver installers offer a “clean installation” option. Alternatively, tools like Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) can perform a thorough clean sweep in Safe Mode before you install new drivers.
In-Game Graphics Settings: Striking the Balance
Most of your FPS gains will come from intelligently adjusting in-game graphics settings. It’s a balancing act between visual fidelity and performance.
Resolution and Upscaling
The display resolution has the most significant impact on FPS. Dropping from 4K to 1440p, or 1440p to 1080p, will yield substantial gains. Modern upscaling technologies like NVIDIA DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) and AMD FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) can offer near-native image quality at lower internal rendering resolutions, providing a massive FPS boost with minimal visual compromise. Always enable these if available in your game and supported by your GPU.
Texture Quality and Filtering
Texture quality dictates how detailed surfaces appear. Higher textures consume more VRAM. If your GPU has ample VRAM (8GB+ for AAA at 1440p/4K), you can often run these at high or ultra without a significant FPS hit. Anisotropic Filtering (AF) affects texture sharpness at an angle; 8x or 16x usually has a minor performance cost for a noticeable visual improvement.
Shadows, Reflections, and Volumetric Effects
These settings are notorious FPS killers. Shadows, especially high-resolution or ray-traced shadows, are very demanding. Reducing shadow quality, turning off elaborate reflections, and lowering volumetric fog/cloud quality can free up a lot of frames.
Anti-Aliasing (AA)
AA methods like MSAA (Multi-Sample Anti-Aliasing) are very taxing. TXAA (Temporal Anti-Aliasing) is less demanding but can introduce blur. FXAA (Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing) is lighter but less effective. If using DLSS/FSR, often you won’t need additional AA, as they handle jagged edges themselves. Experiment with lower AA settings or turn them off if jagged edges aren’t bothersome and you need frames.
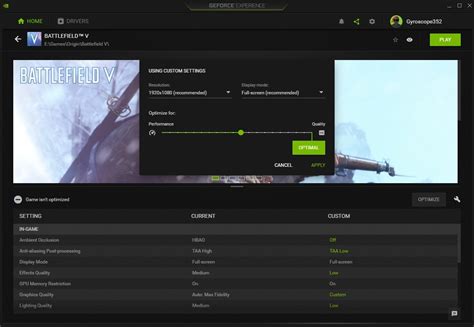
GPU Control Panel Settings: Fine-Tuning Your Card
Both NVIDIA and AMD offer comprehensive control panels that allow you to override or enhance game-specific settings, offering another layer of optimization.
Power Management Mode (NVIDIA) / Power Limit (AMD)
For NVIDIA users, set “Power management mode” to “Prefer maximum performance” in the NVIDIA Control Panel under “Manage 3D settings” > “Global Settings.” This ensures your GPU consistently runs at its highest clock speeds when under load, rather than trying to conserve power. AMD users can achieve similar results by increasing their “Power Limit” in Radeon Adrenalin Software, though this is closer to a mild overclock.
Low Latency Mode (NVIDIA) / Anti-Lag (AMD)
These features reduce input lag by limiting the number of frames queued by the CPU for the GPU. Set NVIDIA’s Low Latency Mode to “On” or “Ultra,” and enable AMD’s Anti-Lag. This won’t directly boost FPS but will make your game feel more responsive, especially at higher frame rates.

Image Sharpening / Radeon Image Sharpening (RIS) / FidelityFX Sharpening
If you’re using DLSS/FSR or playing at a slightly lower resolution, these post-processing filters can help restore some image crispness without a significant performance penalty. Experiment with the intensity to find a balance you like.
Vertical Sync (VSync)
VSync synchronizes your game’s frame rate with your monitor’s refresh rate to prevent screen tearing. However, it can introduce input lag and cap your FPS to your monitor’s refresh rate. If you have a G-Sync or FreeSync monitor, use those adaptive sync technologies instead. If not, and your FPS consistently exceeds your refresh rate, consider disabling VSync for lower input lag, or enabling it if tearing is unbearable.

System-Level Optimizations: Beyond the GPU
Don’t overlook general system health and settings that can indirectly affect your gaming performance.
Windows Game Mode
Ensure Windows Game Mode is enabled (Settings > Gaming > Game Mode). This feature prioritizes your game’s resources and disables background tasks. While its impact can be minimal on high-end systems, it’s worth enabling.
Close Background Applications
Before launching a demanding game, close any unnecessary applications running in the background, such as web browsers, streaming apps, or productivity software. These can consume CPU, RAM, and GPU resources that your game could use.
Overclocking (Advanced)
For experienced users, carefully overclocking your GPU (and CPU/RAM) can yield additional FPS. Use reliable software like MSI Afterburner or AMD’s built-in tuning tools. Always research and proceed with caution, monitoring temperatures closely.
Monitor Your Performance
Tools like MSI Afterburner (with RivaTuner Statistics Server) or the in-game FPS counters (if available) can help you monitor your FPS, GPU usage, VRAM usage, and temperatures. This data is invaluable for understanding the impact of your setting changes.
Conclusion
Boosting FPS in AAA titles is a multi-faceted process that involves a combination of updated drivers, intelligent in-game settings, optimized GPU control panel configurations, and general system hygiene. By systematically working through these tips, you can unlock a smoother, more enjoyable gaming experience without necessarily needing to purchase new hardware. Remember to experiment with settings, as optimal configurations can vary based on your specific hardware, monitor, and individual game.








