How to optimize gaming PC airflow for lower temps & stable FPS?

Why Airflow Matters for Gaming Performance
For any serious PC gamer, a smooth and consistent experience is paramount. Nothing disrupts immersion more than stuttering frames, freezing, or even system crashes, often stemming from overheating components. Effective airflow within your PC case isn’t just about keeping things cool; it’s about safeguarding your hardware’s longevity and ensuring your CPU and GPU can operate at their peak performance without thermal throttling. Optimizing airflow is a critical, yet often overlooked, step towards achieving lower temperatures and, consequently, rock-solid FPS.

Understanding Air Pressure and Fan Placement
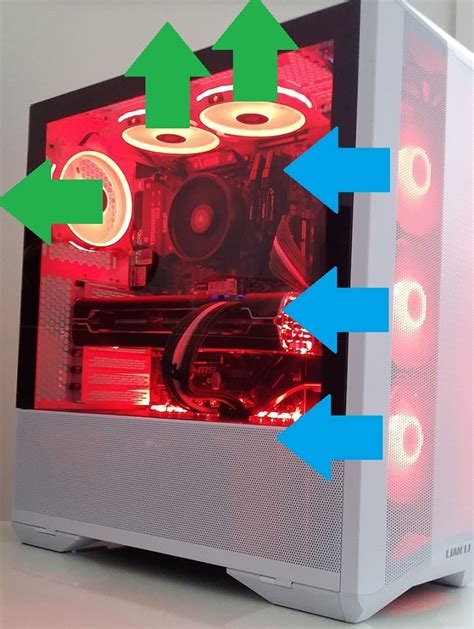
The foundation of good airflow lies in creating a positive or neutral air pressure environment within your case. This dictates how air moves in and out. Generally, you want to create a clear path for cool air to enter, flow over heat-generating components, and then exit. The most common setup involves:
- Intake Fans: Typically located at the front or bottom of the case, these fans draw cool air from outside into the PC.
- Exhaust Fans: Usually positioned at the rear or top, these fans expel hot air from the PC.
A positive pressure setup (more air coming in than going out) helps prevent dust from entering through un-filtered gaps, while a neutral or slightly negative pressure can be effective if combined with good dust filtering. The goal is always to have a consistent, unidirectional flow.
Case Selection & Fan Types
Your PC case is more than just an enclosure; it’s the primary determinant of your system’s airflow potential. Cases with mesh fronts, ample fan mounting options, and good clearance for tall CPU coolers or long GPUs are ideal. Avoid cases with solid front panels that restrict airflow unless they have well-designed side vents.
When it comes to fans, there are two main types:
- Static Pressure Fans: Designed to push air through restrictive spaces, like radiators or dense fin stacks on CPU coolers. They excel at overcoming resistance.
- Airflow Fans: Best for moving large volumes of air through open spaces, such as intake or exhaust points in a case.
A mix of both types, strategically placed, will yield the best results. For instance, static pressure fans on a front radiator and airflow fans for top/rear exhaust.

Cable Management & Dust Control
Cluttered cables are the enemy of good airflow. Bundling and routing cables behind the motherboard tray, or through grommets, clears pathways for air to move freely around your components. Even seemingly minor obstructions can create dead zones where heat can build up. Invest time in proper cable management; it pays dividends in cooling efficiency.
Dust is another significant impediment. Over time, dust accumulates on fan blades, heatsinks, and vents, acting as an insulating layer that traps heat. Regular cleaning (every 3-6 months, depending on your environment) with compressed air is crucial. Ensure your intake fans have dust filters, and clean these filters regularly to maintain optimal airflow without letting debris into your system.

Optimizing Component-Specific Cooling
CPU Cooling:
Whether you use an air cooler or an AIO liquid cooler, ensure it’s properly installed and oriented. For air coolers, the fan should typically push air towards the rear exhaust or top exhaust. For AIOs, mounting the radiator as an intake at the front can provide cooler air to the liquid, but this also means slightly warmer air inside the case. Mounting it as an exhaust at the top or rear removes CPU heat directly from the case.
GPU Cooling:
Most modern GPUs are designed with their own cooling solutions, drawing air from below and exhausting it out the back or sides. Ensure there’s adequate clearance beneath your GPU (especially if it’s a large card) for it to draw in cool air. Sometimes, adding a bottom-mounted intake fan can directly feed cool air to the GPU, significantly dropping its operating temperatures.

Monitoring and Fine-Tuning
The final step in optimizing your airflow is monitoring. Use software like HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or NZXT CAM to keep an eye on your CPU and GPU temperatures under load (e.g., while gaming). Test different fan speed curves using your motherboard’s BIOS or fan control software. Don’t be afraid to experiment with fan orientations or adding/removing fans to find the optimal balance for your specific setup. A few degrees can make a real difference in preventing thermal throttling and maintaining those smooth, stable frame rates you desire.
By taking a systematic approach to airflow optimization, from proper fan placement and selection to meticulous cable and dust management, you’ll ensure your gaming PC runs cooler, quieter, and more reliably, allowing you to enjoy your favorite titles without performance hiccups.