How to optimize GPU settings for max FPS in competitive games?

In the high-stakes world of competitive gaming, every frame per second (FPS) counts. A higher FPS not only makes your game feel smoother and more responsive but can also give you a tangible edge over opponents, allowing for quicker reaction times and more precise aim. While a powerful GPU is the foundation, simply having one isn’t enough; optimizing its settings is key to squeezing out every last frame. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to tweak your GPU settings for maximum FPS in your favorite competitive titles.
Understanding Your Goal: FPS vs. Graphics Fidelity
Before diving into specific settings, it’s crucial to understand the trade-off. For competitive gaming, the priority is almost always FPS over visual fidelity. While beautiful graphics are enjoyable in single-player experiences, they can introduce input lag or stuttering that is detrimental in competitive play. Our goal is to find the sweet spot where you maintain a high, stable frame rate without completely sacrificing the ability to discern important in-game details.

Essential Driver Updates & Software
Keep Your Drivers Current
The first and most critical step is ensuring your graphics drivers are up to date. NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel frequently release driver updates that include performance optimizations for new games and general bug fixes. Always download drivers directly from the manufacturer’s official website.
- NVIDIA: Use GeForce Experience or download from the NVIDIA driver page.
- AMD: Use AMD Radeon Software or download from the AMD drivers & support page.
Performing a clean installation of new drivers is often recommended to prevent potential conflicts with older driver files.
NVIDIA Control Panel / AMD Radeon Software Basics
These powerful tools provide granular control over your GPU’s behavior. Familiarize yourself with them, as many critical optimizations will happen here.
General In-Game Settings Optimization
Many games offer extensive graphics options. Here’s a general hierarchy of what to lower first for the biggest FPS gains:
Resolution and Scaling
- Resolution: Always aim for your monitor’s native resolution (e.g., 1920×1080, 2560×1440). Lowering this significantly reduces visual clarity and can put you at a disadvantage.
- Render Scale/Resolution Scale: If native resolution is too demanding, consider lowering the render scale (e.g., to 90%). This renders the game at a lower resolution internally and then scales it up, offering a balance between performance and visual quality.
Texture Quality and Filtering
Texture quality affects the detail of surfaces. While higher textures look better, they primarily consume VRAM. If you have a GPU with ample VRAM (8GB+), you might be able to keep this relatively high. Anisotropic Filtering (AF) affects how textures look at oblique angles. Set this to 8x or 16x if VRAM allows, as its performance impact is usually minimal.
Shadows, Reflections, and Environmental Details
These are often the biggest FPS killers. Shadows, especially high-resolution ones, are incredibly demanding. Lowering or disabling shadows can yield massive performance improvements. Similarly, reflections and detailed environmental clutter (like foliage density) are resource-intensive. Turn these down or off.
Anti-Aliasing and VSync
- Anti-Aliasing (AA): Reduces jagged edges. Techniques like MSAA or SSAA are very demanding. Opt for less demanding options like FXAA or TAA, or disable it entirely if you prioritize raw FPS.
- VSync: Synchronizes your game’s frame rate with your monitor’s refresh rate to prevent screen tearing. However, it can introduce input lag. If you have a high refresh rate monitor (144Hz+) and your FPS consistently exceeds it, consider disabling VSync, especially if you have G-Sync or FreeSync.
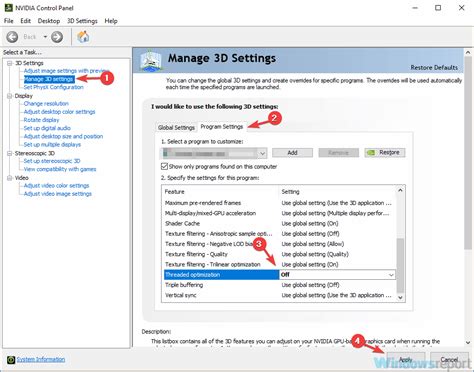
Advanced GPU Control Panel Settings
Now, let’s dive into specific settings within your GPU’s control panel:
Power Management Mode (NVIDIA) / Power Efficiency (AMD)
- NVIDIA (3D Settings > Power Management Mode): Set this to ‘Prefer maximum performance’. This ensures your GPU always runs at its highest clock speeds, preventing throttling.
- AMD (Gaming > Global Graphics > Power Efficiency): Disable this to allow your GPU to consume more power for sustained performance.
Low Latency Mode (NVIDIA) / Anti-Lag (AMD)
- NVIDIA (3D Settings > Low Latency Mode): Set to ‘Ultra’. This can significantly reduce input lag by limiting the number of frames queued by the CPU for the GPU.
- AMD (Gaming > Global Graphics > Radeon Anti-Lag): Enable this for a similar reduction in input lag.
Image Sharpening / Radeon Boost
- NVIDIA (3D Settings > Image Sharpening): You can experiment with this, as it can make lower-resolution images appear crisper with minimal performance cost.
- AMD (Gaming > Global Graphics > Radeon Boost): This dynamically lowers resolution during fast-motion scenes, boosting FPS without a noticeable visual impact for many. Enable it for competitive games.
Testing and Fine-Tuning
Benchmarking and Monitoring
After adjusting settings, test them! Use in-game benchmarks (if available) or monitoring software like MSI Afterburner, HWiNFO, or GeForce Experience’s FPS counter to track your frame rates and GPU utilization. Play a few rounds of your competitive game to get a real-world feel for the changes.
Iterative Adjustments
Optimization is an iterative process. Adjust one or two settings at a time, test, and then refine. If your FPS is consistently high and stable, you might even be able to incrementally increase some visual settings without losing performance. If you experience stutters or drops, revert the last change.

Conclusion
Optimizing your GPU settings for maximum FPS in competitive games is a critical step for serious players. By systematically updating drivers, tweaking in-game options, and fine-tuning advanced GPU control panel settings, you can unlock a smoother, more responsive gaming experience. Remember, consistency and stability are key. With a little patience and experimentation, you’ll be well on your way to dominating the leaderboards with every frame per second at your command.








