How to optimize GPU settings for max FPS in new AAA games?
Mastering Your GPU for Peak Gaming Performance
Modern AAA games push graphical fidelity to new heights, often demanding significant horsepower from your GPU. While a powerful graphics card is a great start, optimizing its settings is crucial to squeeze every possible frame per second (FPS) and ensure a smooth, immersive gaming experience. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to fine-tune your GPU for maximum FPS without sacrificing too much visual quality.
1. Update Your GPU Drivers Religiously
This is arguably the most critical and often overlooked step. Both NVIDIA and AMD frequently release new drivers specifically optimized for the latest game releases, often providing significant performance boosts and bug fixes. Always ensure you are running the most up-to-date drivers for your graphics card. You can download them directly from NVIDIA’s or AMD’s official websites or use their respective software (GeForce Experience or Radeon Software) to manage updates.
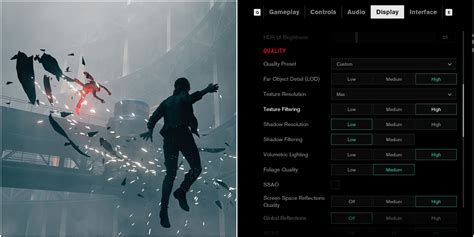
2. Tweak In-Game Graphics Settings Intelligently
Every game offers a plethora of graphical options, and understanding which ones have the biggest impact on FPS is key. It’s about finding a balance between visual fidelity and performance.
- Resolution: The most impactful setting. Running at your monitor’s native resolution is ideal, but if FPS is a major issue, consider dropping it slightly or using resolution scaling features (e.g., DLSS, FSR) if available.
- Texture Quality: This setting primarily affects VRAM usage. If you have a GPU with sufficient VRAM (e.g., 8GB+ for 1080p/1440p), you can often set this to High or Ultra with minimal FPS impact. Lowering it can help if you’re VRAM limited.
- Shadow Quality: Shadows are notoriously demanding. Dropping shadow quality from Ultra to High or even Medium can provide a noticeable FPS boost with a relatively small visual downgrade.
- Anti-Aliasing (AA): Techniques like MSAA are very performance-intensive. FXAA or TAA are less demanding alternatives. If a game offers DLSS, FSR, or XeSS, these are often the best options as they provide excellent image quality with an FPS uplift.
- Ambient Occlusion (AO): Adds realistic depth to objects but can be resource-heavy. HBAO+ or SSAO can hit performance; reducing or disabling it can free up frames.
- Volumetric Lighting/Fog: These effects add atmosphere but are extremely taxing. Lowering their quality or disabling them entirely can yield significant gains.
- Ray Tracing: While visually stunning, ray tracing is the most demanding feature in modern games. If FPS is your priority, disabling ray tracing entirely is often necessary.
- Post-Processing Effects: Things like motion blur, depth of field, and lens flare can be disabled without much visual loss and can sometimes offer minor FPS improvements.

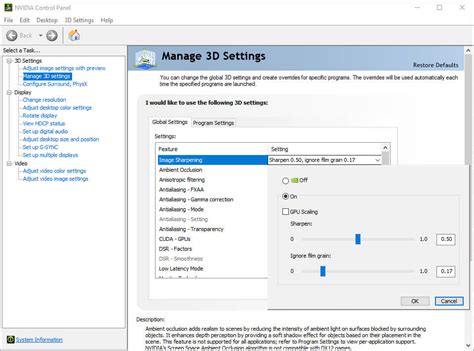
3. Optimize Via GPU Control Panels (NVIDIA Control Panel / AMD Radeon Software)
Beyond in-game settings, your GPU’s control panel offers global settings that can affect all games.
NVIDIA Control Panel:
- Power Management Mode: Set to ‘Prefer maximum performance’ under ‘Manage 3D settings’ > ‘Global Settings’. This ensures your GPU always runs at its highest clock speeds.
- Low Latency Mode: Experiment with ‘On’ or ‘Ultra’ (if available). This can reduce input lag but might introduce micro-stutters in some systems.
- Texture Filtering – Quality: Set to ‘High performance’ instead of ‘Quality’ for a slight FPS boost.
- Image Scaling (NIS): If you need to run games at a lower internal resolution for performance, NIS can upscale them with sharpening, offering a crisper image than standard upscaling.
AMD Radeon Software:
- Radeon Anti-Lag: Similar to NVIDIA’s Low Latency Mode, it can reduce input lag.
- Radeon Boost: Dynamically lowers resolution in fast-motion scenes to improve FPS without a major visual impact.
- Image Sharpening (RSR): AMD’s equivalent to NIS, offering resolution scaling and sharpening.
- Texture Filtering Quality: Set to ‘Performance’ for a slight FPS gain.
4. Monitor and Maintain Your GPU
Keeping an eye on your GPU’s performance and health is crucial for sustained high FPS.
- Monitor Temperatures: High temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, where your GPU automatically reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating, causing FPS drops. Use tools like MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor to keep an eye on temps. Aim for below 80-85°C under load.
- Clean Your PC: Dust accumulation in your GPU’s heatsink and case fans can severely impair cooling. Regular cleaning (every 3-6 months) is recommended.
- Consider a Custom Fan Curve: Using tools like MSI Afterburner, you can create a custom fan curve that ramps up fan speeds more aggressively at higher temperatures, keeping your GPU cooler.
- Overclocking (Advanced): For advanced users, safely overclocking your GPU can provide an additional 5-15% performance boost. However, this carries risks and should only be done with proper research and caution.

5. Don’t Forget System-Wide Considerations
While the GPU is the primary focus, other components can bottleneck performance:
- CPU: A weak CPU can limit your GPU’s potential, especially in CPU-intensive games.
- RAM: Ensure you have sufficient RAM (16GB is the current sweet spot for AAA gaming) and that it’s running at its advertised speed (XMP/DOCP enabled in BIOS).
- Storage: While it doesn’t directly impact FPS, a fast SSD will drastically reduce load times and improve overall system responsiveness, especially in open-world games.
- Background Processes: Close unnecessary applications and background processes while gaming to free up CPU and RAM resources.

Conclusion
Optimizing your GPU for maximum FPS in new AAA games is an ongoing process of experimentation. Start with driver updates, then tackle in-game settings, followed by global control panel adjustments. Always monitor your performance and temperatures, and don’t be afraid to tweak settings to find the perfect balance for your system and your preferred games. With these steps, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying buttery-smooth gameplay in the latest titles.








