How to reduce input lag and ensure G-Sync/FreeSync is properly configured for gaming?
The Quest for Lag-Free Gaming
In the competitive world of PC gaming, every millisecond counts. Input lag, the delay between your input (e.g., mouse click, key press) and its corresponding action appearing on screen, can be the difference between victory and defeat. Coupled with the desire for buttery-smooth visuals, properly configuring adaptive sync technologies like NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync is crucial for an optimal gaming experience. This guide will walk you through the steps to minimize input lag and ensure your adaptive sync setup is flawless.
Understanding and Minimizing Input Lag
Input lag can originate from various sources, including your display, mouse, keyboard, graphics card, operating system, and even the game itself. Reducing it involves a multi-pronged approach targeting each potential bottleneck.
Monitor Settings
- Game Mode: Many modern monitors have a ‘Game Mode’ or similar setting designed to reduce processing time. Enable it.
- Overdrive/Response Time: Experiment with your monitor’s overdrive setting. Too low, and you get ghosting; too high, and you might see overshoot. Find the sweet spot for your panel.
- Disable Image Enhancements: Turn off any post-processing features like dynamic contrast, sharpening, or noise reduction, as these add latency.
In-Game & System Settings
- Graphics Settings: While high settings look good, they can increase GPU processing time, potentially leading to more lag if your system struggles. Lowering some demanding settings can help.
- V-Sync: Generally, avoid V-Sync when using G-Sync/FreeSync, as it adds input lag. Instead, rely on adaptive sync.
- Frame Rate Cap: Cap your frame rate slightly below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate (e.g., 141 FPS for a 144Hz monitor) to keep G-Sync/FreeSync active and prevent V-Sync from engaging.
- Exclusive Fullscreen: Play games in exclusive fullscreen mode whenever possible, as it gives the game direct control over your display, often reducing latency compared to borderless windowed mode.

G-Sync and FreeSync: Adaptive Sync Explained
G-Sync (NVIDIA) and FreeSync (AMD) are adaptive synchronization technologies that eliminate screen tearing and stuttering by synchronizing your monitor’s refresh rate with your GPU’s frame rate. This ensures that frames are displayed as soon as they are rendered, providing a smoother and more responsive visual experience, especially when frame rates fluctuate.
Proper Configuration for NVIDIA G-Sync
If you have an NVIDIA graphics card and a G-Sync compatible monitor:
- Enable G-Sync on Monitor: Check your monitor’s OSD (On-Screen Display) menu to ensure G-Sync is enabled.
- Open NVIDIA Control Panel: Right-click on your desktop and select ‘NVIDIA Control Panel’.
- Set up G-SYNC: Navigate to ‘Display’ -> ‘Set up G-SYNC’.
- Enable G-SYNC: Check the box for ‘Enable G-SYNC, G-SYNC Compatible’.
- Select Display: Choose your primary gaming monitor.
- Apply: Select whether to enable G-SYNC for full-screen mode only or both full-screen and windowed modes (full-screen is generally recommended for performance). Click ‘Apply’.
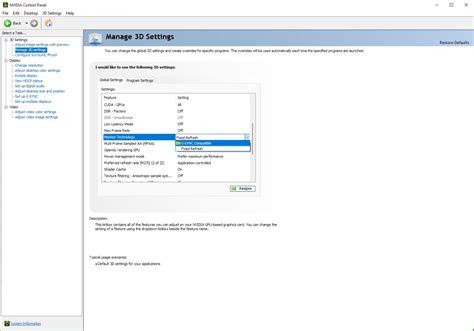
- Manage 3D Settings: Go to ‘3D Settings’ -> ‘Manage 3D settings’.
- Monitor Technology: Ensure ‘Monitor Technology’ is set to ‘G-SYNC’.
- Max Frame Rate: Set a ‘Max Frame Rate’ globally or for specific games, typically 3 FPS below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate (e.g., 141 FPS for 144Hz). This ensures you stay within the G-Sync range.
- Low Latency Mode: Experiment with ‘Low Latency Mode’. ‘On’ can reduce lag, while ‘Ultra’ might introduce some minor frame pacing issues for some, but offers the lowest latency.

Proper Configuration for AMD FreeSync
If you have an AMD graphics card and a FreeSync compatible monitor:
- Enable FreeSync on Monitor: Access your monitor’s OSD menu and ensure FreeSync (or Adaptive Sync) is enabled.
- Open AMD Radeon Software: Right-click on your desktop and select ‘AMD Radeon Software’.
- Navigate to Display Tab: Click on the ‘Settings’ gear icon in the top right, then select the ‘Display’ tab.
- Enable FreeSync: Toggle ‘Radeon FreeSync’ to ‘Enabled’ for your primary monitor.
- Gaming Profile Settings: Go to the ‘Gaming’ tab and select ‘Global Graphics’.
- Radeon Anti-Lag / Boost: Experiment with ‘Radeon Anti-Lag’ and ‘Radeon Boost’ for potential input lag reduction.
- Frame Rate Target Control (FRTC): If available, set a global or per-game FRTC slightly below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate (e.g., 141 FPS for 144Hz) to keep FreeSync active.
Troubleshooting and Best Practices
- Check Cables: Always use DisplayPort for G-Sync and FreeSync. Ensure your cable is rated for your monitor’s refresh rate and resolution.
- Driver Updates: Keep your graphics drivers updated to the latest stable version.
- Monitor Firmware: Check your monitor manufacturer’s website for any firmware updates.
- Test Games: Play a variety of games to confirm the settings are working as expected. Look for the absence of tearing and a generally smoother feel.
- Low Frame Rate Compensation (LFC): Ensure your monitor supports LFC if its FreeSync range is not wide (e.g., 48-144Hz). LFC helps FreeSync remain active even if your frame rate drops below the minimum threshold by multiplying frames.
Conclusion
By diligently configuring your monitor settings, in-game options, and leveraging the power of G-Sync or FreeSync, you can significantly reduce input lag and achieve an incredibly fluid and responsive gaming experience. Take the time to fine-tune these settings, and you’ll find yourself enjoying your favorite titles more than ever, with every input feeling precise and instantaneous.









