How to stop my gaming PC from overheating during long sessions?

The Silent Killer of Gaming Performance: Understanding PC Overheating
Long, intense gaming sessions are a joy for any enthusiast, but they can push your PC’s hardware to its limits. One of the most insidious enemies of your gaming rig is overheating. When components like your CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) get too hot, they can suffer from performance throttling, instability, and even permanent damage over time. Understanding the signs and causes of overheating is the first step towards a cooler, more stable gaming experience.

Common Causes of Overheating in Gaming PCs
Several factors contribute to a PC’s internal temperature rising beyond safe limits. The most prevalent culprits include:
- Dust Buildup: Over time, dust accumulates on fans, heatsinks, and vents, acting as an insulating layer that traps heat and restricts airflow.
- Poor Airflow: Inadequate case fan setup (e.g., more exhaust than intake, or vice-versa), obstructed vents, or tightly packed components can create stagnant hot spots.
- Degraded Thermal Paste: The thermal paste between your CPU/GPU and their respective heatsinks can dry out and become less effective, hindering heat transfer.
- Aging or Inefficient Coolers: Stock coolers might not be sufficient for high-performance components, especially when overclocked. Fans can also wear out and become less effective.
- High Ambient Temperatures: If your room is hot, your PC will naturally struggle more to dissipate heat.
Immediate Steps: Cleanliness and Monitoring
Before considering upgrades, ensure your existing setup is performing optimally. Start with these fundamental checks:
1. Clean Your PC Thoroughly
The simplest and often most effective solution is a deep clean. Use compressed air to blow out dust from all fans (CPU, GPU, case fans), heatsinks, and power supply unit (PSU). Hold fan blades gently to prevent over-spinning them while cleaning. Pay close attention to the fins of your CPU and GPU coolers.
2. Check Fan Functionality
Ensure all case fans, CPU cooler fans, and GPU fans are spinning correctly and are free from obstructions. Listen for unusual noises, which could indicate a failing fan bearing.
3. Monitor Temperatures
Install monitoring software like HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or NZXT CAM to keep an eye on your CPU and GPU temperatures while gaming. Ideal temperatures are typically below 70-80°C under load, though this can vary by component. High temperatures consistently hitting 90°C+ are a red flag.

Optimizing Airflow and Cooling Hardware
Once your PC is clean and you’re monitoring temperatures, it’s time to think about enhancing its cooling capabilities.
1. Improve Case Airflow
Ensure you have a balanced airflow setup. Generally, more intake fans at the front/bottom and exhaust fans at the top/rear create positive pressure, which helps keep dust out and pushes hot air efficiently. Good cable management is crucial here; bundles of cables can act as barriers to airflow.
2. Upgrade CPU Cooler
If your CPU consistently runs hot, consider upgrading from a stock cooler to an aftermarket air cooler (like those from Noctua or be quiet!) or an All-in-One (AIO) liquid cooler. These offer significantly better heat dissipation.
3. Consider GPU Cooling Solutions
While most GPUs come with robust cooling, some models can run hotter than desired. Ensure your case has good airflow to the GPU. In extreme cases, aftermarket GPU coolers or even custom water loops can be installed, though this is a more advanced modification.

Software and Settings Adjustments
Hardware isn’t the only factor; software settings can also play a vital role in thermal management.
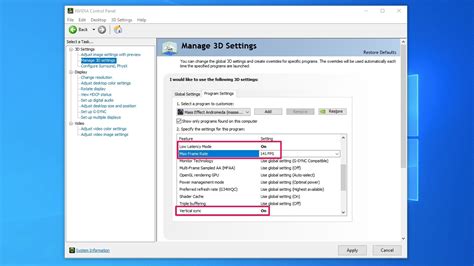
1. Adjust Fan Curves
Most motherboards and GPU utilities (e.g., MSI Afterburner, ASUS GPU Tweak) allow you to customize fan speed curves based on temperature. Set your fans to spin faster at higher temperatures to actively dissipate heat before it becomes critical.
2. Undervolting Your CPU/GPU
Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to your CPU or GPU without sacrificing significant performance. Lower voltage directly translates to less heat generation. This requires careful testing but can yield impressive temperature drops.
3. Tweak In-Game Settings
If you’re still struggling, slightly reducing demanding graphical settings like anti-aliasing, shadow quality, or rendering resolution can significantly lower the load on your GPU, thus reducing its heat output.

Long-Term Maintenance for a Cool Rig
To keep your gaming PC cool for years to come, incorporate these maintenance practices:
1. Replace Thermal Paste
Every few years, the thermal paste on your CPU and GPU can dry out and lose effectiveness. Replacing it is a relatively simple procedure that can significantly improve heat transfer. High-quality thermal paste can make a noticeable difference.
2. Regular Dusting Schedule
Make it a habit to clean your PC every 3-6 months, or more frequently if you live in a dusty environment or have pets.
3. Check for Firmware Updates
BIOS/UEFI and GPU VBIOS updates sometimes include thermal management improvements or fan control enhancements.

Conclusion
An overheating gaming PC isn’t just an annoyance; it’s a threat to your hardware’s lifespan and performance. By diligently cleaning your system, optimizing airflow, considering cooling upgrades, and making smart software adjustments, you can ensure your rig stays frosty even during the most demanding long gaming sessions. A well-maintained and cool PC will provide a more consistent, enjoyable, and durable gaming experience, allowing you to focus on the game, not the heat.