My gaming FPS is low. How do I troubleshoot PC performance bottlenecks for smoother gameplay?

Few things are as frustrating for a PC gamer as experiencing stuttering, lag, or consistently low Frames Per Second (FPS). It can turn an immersive experience into a slideshow and severely impact your enjoyment and competitive edge. The good news is that most low FPS issues can be identified and often resolved with systematic troubleshooting. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to pinpoint and address the performance bottlenecks affecting your gaming PC.
1. Start with the Basics: Software & Settings
Before diving deep into hardware, ensure your software foundation is solid. Often, the simplest fixes yield the biggest improvements.
Update Your Drivers
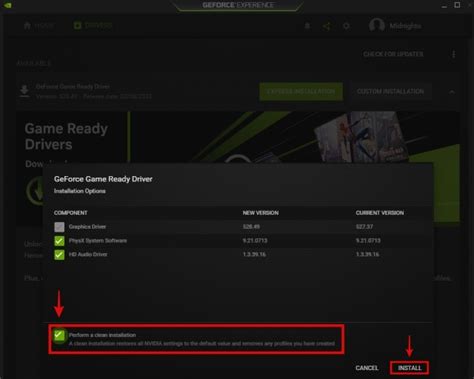
Outdated or corrupted graphics drivers are a leading cause of poor gaming performance. Always download the latest drivers directly from NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel’s websites. Don’t forget to update your chipset drivers as well, usually found on your motherboard manufacturer’s support page.
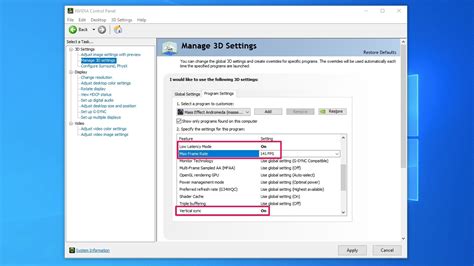
Adjust In-Game Settings
Many games offer a plethora of graphics options. Start by lowering settings like texture quality, shadow quality, anti-aliasing, and view distance. Experiment with each setting individually to see its impact on FPS. Sometimes, a single setting like ray tracing or a very high resolution can cripple performance.
Close Background Applications
Programs running in the background (web browsers, streaming apps, torrent clients, etc.) consume CPU, RAM, and GPU resources. Close unnecessary applications before launching your game. Check Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) for resource-intensive processes.
Power Management Settings
Ensure your Windows power plan is set to ‘High Performance’ or ‘Ultimate Performance’. This prevents your CPU and GPU from throttling down to save power, which can limit their maximum potential during gaming.
2. Identify Hardware Bottlenecks
If software adjustments don’t solve the problem, it’s time to investigate your PC’s components. A bottleneck occurs when one component limits the performance of others.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
A CPU bottleneck happens when your processor can’t feed data to the GPU fast enough. This often results in your GPU not reaching 99-100% utilization. Monitor CPU usage during gameplay; consistently high CPU usage (e.g., above 90%) across multiple cores can indicate a bottleneck or thermal throttling.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
The GPU is usually the primary factor in gaming FPS. If your GPU is consistently at 99-100% utilization, it means it’s working as hard as it can, and it’s likely your bottleneck. While this isn’t always bad (it means you’re maximizing its potential), if your FPS is still low, it suggests your GPU simply isn’t powerful enough for your desired settings/resolution.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Insufficient RAM (e.g., less than 16GB for modern gaming) or slow RAM speeds can lead to stutters and load time issues. Monitor RAM usage; if it frequently hits its limit, your system might be offloading data to the much slower page file on your drive.
Storage Drive
While an older HDD won’t directly impact FPS once a game is loaded, it can cause longer load times and occasional stutters if game assets aren’t loaded quickly enough. Upgrading to an SSD is a significant quality-of-life improvement for gaming.

3. Utilize Monitoring Tools
To accurately identify bottlenecks, you need data. Several tools can help you monitor your system’s performance in real-time:
- MSI Afterburner (with RivaTuner Statistics Server): This is the gold standard for monitoring GPU, CPU, RAM, and FPS overlays during gameplay. You can customize what information is displayed on your screen.
- HWMonitor / HWiNFO: These tools provide detailed information on CPU and GPU temperatures, clock speeds, voltages, and usage. They are excellent for identifying thermal throttling.
- Task Manager (Windows): Basic but useful for a quick glance at CPU, RAM, Disk, and GPU usage (in newer Windows versions).
Interpreting the Data:
- High GPU Usage (95-100%) & Low FPS: Your GPU is the bottleneck. Lower graphics settings or consider upgrading.
- Low GPU Usage (e.g., 60%) & High CPU Usage (90%+) & Low FPS: Your CPU is the bottleneck. Consider upgrading your CPU or motherboard/RAM if it’s an older platform.
- High Temperatures (CPU/GPU): If your CPU or GPU temperatures are consistently above 85-90°C, they might be thermal throttling, reducing performance to prevent damage. Improve cooling with better case airflow, CPU cooler, or cleaning dust.
4. Advanced Troubleshooting & Optimization
Once you have identified the primary bottleneck, there are further steps you can take.
Clean Your PC
Dust buildup in your case, on heatsinks, and fan blades can severely impede cooling, leading to higher temperatures and thermal throttling. Regular cleaning is crucial.
Check for Malware/Viruses
Malicious software can consume system resources, leading to performance degradation. Run a full scan with reputable antivirus software.
Windows Game Mode & Visual Effects
Windows 10/11 includes a ‘Game Mode’ designed to optimize your PC for gaming. Ensure it’s enabled. Also, consider adjusting visual effects in Windows (Performance Options > Adjust for best performance) to free up minor resources.
BIOS/UEFI Settings
Ensure XMP/DOCP is enabled for your RAM to run at its advertised speeds. Check for any CPU settings that might limit performance, though generally, default settings are fine.
Overclocking (Use with Caution)
Carefully overclocking your CPU or GPU can provide a performance boost, but it increases heat and power consumption and carries risks if not done correctly. Only attempt this if you are comfortable and have adequate cooling.

5. When All Else Fails: Consider Upgrades
If you’ve systematically gone through all troubleshooting steps and still experience low FPS, it’s possible your hardware simply isn’t powerful enough for your gaming demands. Based on your bottleneck analysis, prioritize upgrading the component that’s holding your system back the most – whether it’s the GPU, CPU, or adding more RAM.

Conclusion
Troubleshooting low FPS can be a daunting task, but by approaching it methodically, you can often significantly improve your gaming experience. Start with software, move to monitoring hardware, interpret the data, and then apply targeted solutions. With a bit of patience and experimentation, you’ll be on your way to smoother, more enjoyable gameplay.