What are the optimal NVIDIA/AMD driver settings for maximum in-game FPS and stability?

Unlocking Peak Gaming Performance: Driver Settings Explained
Achieving the highest possible in-game Frames Per Second (FPS) while maintaining rock-solid stability is the holy grail for any PC gamer. While raw hardware power is fundamental, the software driving that hardware—your graphics card drivers—plays an equally critical role. Both NVIDIA and AMD offer a suite of customizable settings within their respective control panels that can significantly impact your gaming experience. Understanding and correctly configuring these settings can turn a good gaming session into a great one.
NVIDIA Control Panel: Precision Tuning for GeForce GPUs
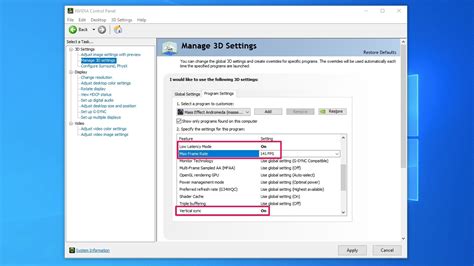
For NVIDIA users, the NVIDIA Control Panel is your command center. Access it by right-clicking on your desktop. Here are the key settings to focus on under “Manage 3D settings” (it’s often best to adjust “Program Settings” for individual games rather than “Global Settings” to avoid conflicts):
- Low Latency Mode: Set to Ultra for competitive games. This minimizes render-ahead frames, reducing input lag at the cost of potentially lower maximum FPS if your GPU is bottlenecked. For less demanding games or if you experience stuttering, try On or Off.
- Max Frame Rate: Capping your FPS slightly below your monitor’s refresh rate (or a stable achievable rate) can improve frame pacing and reduce tearing, even with V-Sync off.
- Power Management Mode: Set to Prefer maximum performance. This ensures your GPU consistently operates at its highest clock speeds, preventing downclocking during intense moments.
- Texture Filtering – Quality: Set to High Performance for maximum FPS, or Quality if visual fidelity is a higher priority and you have GPU headroom.
- Vertical Sync (V-Sync): Generally, leave Off unless you experience severe screen tearing and don’t have G-Sync/FreeSync. If you have an adaptive sync monitor, ensure G-Sync is enabled in the NVIDIA Control Panel and V-Sync is off globally but can be enabled in-game for G-Sync to properly cap FPS at your monitor’s refresh rate.
- Shader Cache Size: Set to Driver Default or a larger size (e.g., 10GB) if available. This helps store compiled shaders, reducing in-game stutter.

AMD Radeon Software: Empowering Radeon Graphics
AMD users will navigate through the AMD Radeon Software. Right-click on your desktop and select “AMD Radeon Software.” Head to the “Gaming” tab and then “Global Graphics” for overall settings, or select specific games for per-profile adjustments.
- Radeon Anti-Lag: Similar to NVIDIA’s Low Latency Mode, Anti-Lag reduces input-to-display response time by dynamically adjusting frame pacing. Enable it for a more responsive feel, especially in competitive titles.
- Radeon Boost: Dynamically lowers resolution in fast-motion scenes to improve FPS. Useful for performance gains without a noticeable visual impact during intense moments.
- Radeon Chill: This feature allows you to set a minimum and maximum FPS target. It can save power and reduce heat, and smooth out frame times when your GPU isn’t fully utilized. Use it for a quieter, cooler experience, but potentially at the cost of absolute maximum FPS.
- Image Sharpening: Enhances visual clarity with minimal performance impact. Experiment with the sharpness level to find a balance you like.
- Enhanced Sync: An alternative to V-Sync, it aims to reduce tearing and input lag, but can sometimes cause stuttering or black screens on certain setups. Test carefully.
- Texture Filtering Quality: Choose Performance for higher FPS or Standard/High for better visuals.

Universal Optimization Strategies for Both NVIDIA and AMD
Beyond brand-specific settings, several practices apply to all graphics cards for optimal gaming performance and stability:
- Keep Drivers Updated: Always use the latest stable drivers from NVIDIA or AMD. These often include performance optimizations for new games and crucial bug fixes.
- Perform Clean Installations: When updating drivers, especially if you’re experiencing issues, choose the “Custom” or “Clean Installation” option. This removes old driver remnants that can cause conflicts.
- Monitor Temperatures: High GPU or CPU temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, severely impacting performance. Use monitoring software (e.g., MSI Afterburner, HWMonitor) to keep an eye on temps. Ensure adequate case airflow.
- In-Game Settings vs. Driver Settings: Driver settings typically provide a baseline, but in-game graphics settings have the most significant impact on FPS. Start with lower in-game settings (especially demanding ones like shadows, volumetric clouds, anti-aliasing) and gradually increase them.
Balancing FPS and Stability: A Delicate Act
While maximizing FPS is often the goal, pushing your system too hard can lead to instability, crashes, or severe stuttering. The optimal settings are a balance specific to your hardware, game, and personal preference.
- Test Systematically: Change one setting at a time and test its impact. Use in-game benchmarks or third-party tools to measure FPS.
- Avoid Overclocking (Initially): If you’re chasing stability, ensure your GPU and CPU are running at stock speeds before tweaking driver settings. Introduce overclocking gradually after achieving a stable baseline.
- Prioritize Core Settings: Focus on the most impactful settings like power management, low latency/anti-lag, and texture quality first.

Advanced Considerations for Modern Systems
Modern operating systems and GPUs introduce additional features that can influence performance:
- Hardware-accelerated GPU Scheduling (HAGS): Found in Windows 10/11 Graphics settings, HAGS offloads some GPU scheduling tasks from the CPU to the GPU. This can free up CPU resources and potentially reduce input lag. Its impact varies by system and game, so test it.
- Resizable BAR / Smart Access Memory (SAM): If your system supports it (Ryzen 5000 series with Radeon 6000/7000 series, or Intel 10th gen+ with NVIDIA 30/40 series), enabling this feature allows the CPU to access the entire GPU memory, potentially boosting performance in certain titles. Ensure it’s enabled in your motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI.

Conclusion
Optimizing your NVIDIA or AMD graphics driver settings is an essential step in fine-tuning your PC for the best possible gaming experience. By meticulously adjusting settings like low latency modes, power management, and texture quality, and combining these with good maintenance practices, you can significantly boost FPS and enhance stability. Remember that the “optimal” settings can be subjective and vary between games and hardware configurations, so don’t be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you.