What monitor settings optimize visuals & responsiveness for competitive FPS games?

In the high-stakes world of competitive First-Person Shooter (FPS) games, every millisecond and every pixel can mean the difference between victory and defeat. While powerful hardware and a stable internet connection are fundamental, optimizing your monitor settings is often an overlooked yet critical component of a winning setup. The goal is to strike a perfect balance: visuals clear enough to spot enemies instantly, and responsiveness so high that your actions translate to the screen without a moment’s delay.
The Foundation: Refresh Rate & Response Time
These two settings are paramount for the core feel of any competitive FPS. Your monitor’s refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), dictates how many times per second the screen can update its image. For competitive play, a minimum of 144Hz is highly recommended, with 240Hz or even 360Hz offering progressively smoother motion and reduced motion blur. Higher refresh rates provide a clearer picture of fast-moving targets and an earlier perception of enemy movements, giving you a crucial edge.
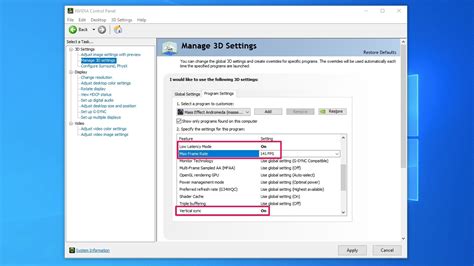
Equally important is response time, typically measured in milliseconds (ms) from gray-to-gray (GtG). This refers to how quickly a pixel can change from one color to another. A lower response time (ideally 1ms GtG) is vital to minimize “ghosting” or “smearing” – the blurry trails left by fast-moving objects. Ghosting can obscure enemy outlines and make target tracking much more difficult. Ensure your monitor is set to its lowest response time mode in its OSD (On-Screen Display) settings.

Minimizing Input Lag & Ghosting with Overdrive
Input lag is the delay between your action (e.g., mouse click) and that action being reflected on screen. While a quality monitor inherently has low input lag, certain settings can affect it. Generally, disable any unnecessary image processing features like dynamic contrast or noise reduction, as these often add latency.
Overdrive (OD), sometimes called Response Time Compensation (RTC), is a feature designed to accelerate pixel transitions even further. While it aims to reduce ghosting, setting it too high can lead to “inverse ghosting” or “overshoot,” where pixels overcompensate and create a bright halo around moving objects. You’ll need to experiment with your monitor’s overdrive settings (usually low, medium, high, or numerical values) to find the “sweet spot” that minimizes ghosting without introducing inverse ghosting. This often involves trial and error in-game or using dedicated test patterns.

Leveraging Adaptive Sync: G-Sync & FreeSync
Adaptive Sync technologies like NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync synchronize your monitor’s refresh rate with your GPU’s frame rate. This eliminates screen tearing and reduces stuttering, leading to a much smoother visual experience. For competitive FPS, the benefits are debated. While eliminating tearing is great, some professional players argue that it introduces a marginal amount of input lag compared to running with V-Sync off and uncapped frame rates. However, if your frame rate fluctuates significantly, Adaptive Sync can provide a more consistent and less distracting visual flow. Most users will find the benefits outweigh any negligible input lag, especially if they can maintain high frame rates within their monitor’s Adaptive Sync range.

Optimizing Visual Clarity: Brightness, Contrast & Color
While responsiveness is key, visuals must remain clear and distinguishable. Brightness should be set to a comfortable level that doesn’t strain your eyes but is bright enough to reveal details in darker areas. Contrast helps differentiate objects; aim for a setting that provides good depth without crushing blacks or blowing out whites.
Gamma impacts the brightness of mid-tones and shadow detail. Adjusting it can help you spot enemies lurking in dark corners, but setting it too high can make the image appear washed out, while too low can obscure important details. Similarly, color vibrance/saturation is largely personal preference; some players slightly boost it to make enemy models “pop” more, while others prefer a more natural look. Features like Black Equalizer (or similar terms) found on many gaming monitors can specifically brighten dark areas without affecting the rest of the image, which can be a game-changer for visibility in certain maps, but use it judiciously to avoid creating a washed-out look. Always disable any “dynamic contrast” or “power saving” features as they typically hinder performance and introduce input lag.

Resolution, Scaling & Additional Settings
Always run your monitor at its native resolution (e.g., 1920×1080 for a 1080p monitor). Running at a lower resolution will make the image appear blurry and pixelated, making enemy identification difficult. If you must use a lower resolution for performance reasons, ensure your GPU handles the scaling rather than the monitor, as GPU scaling is generally faster. Disable any monitor-provided crosshairs or aim assists, as these are often considered unfair and can be distracting. Sharpening settings can sometimes make edges appear more defined, but too much can introduce artifacts; often, it’s best left off or at a very low level.

Finding Your Personal Sweet Spot
Optimizing monitor settings for competitive FPS games is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Every monitor is different, and personal preference plays a significant role. The best approach is to test various settings in your favorite games, paying close attention to how they impact both your visual clarity and perceived responsiveness. Experiment with the overdrive levels, test Adaptive Sync on and off, and fine-tune your brightness and gamma. Remember to also check your in-game video settings, as they interact directly with your monitor’s capabilities. With careful adjustment, you can unlock your monitor’s full potential, enhancing your performance and immersing you deeper into the competitive arena.