Why is my gaming PC stuttering or getting low FPS in new titles, and how can I fix it?

Understanding Performance Hitches in New Titles
There’s nothing more frustrating for a PC gamer than eagerly launching a highly anticipated new title, only to be met with choppy gameplay, erratic frame rates, and frustrating stutters. While modern games push the boundaries of graphical fidelity and computational demands, experiencing poor performance on what you believe should be a capable system can be baffling. This guide will walk you through the most common culprits behind stuttering and low FPS in new PC games and provide actionable steps to get your rig running smoothly.

Common Causes of Stuttering and Low FPS
1. Outdated or Corrupt Drivers
The number one reason for performance issues is often outdated or corrupt graphics drivers. New games frequently leverage the latest features and optimizations provided by NVIDIA and AMD, and older drivers simply aren’t equipped to handle them efficiently. Similarly, outdated chipset drivers can impact overall system communication.
2. Hardware Limitations
While your PC might have handled older games just fine, new titles often demand significantly more from your CPU, GPU, and even RAM. If any of these components are below the game’s recommended specifications, or if your RAM capacity or speed is insufficient, you’ll likely encounter bottlenecks.
3. Overheating Components
When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, they automatically throttle their performance to prevent damage. This thermal throttling can manifest as sudden, severe FPS drops or persistent stuttering, especially during intense gaming sessions.
4. Background Processes and Software Conflicts
Other applications running in the background, such as web browsers, streaming software, antivirus scans, or even system updates, can hog CPU cycles, RAM, or disk I/O, leaving fewer resources for your game.
5. Suboptimal In-Game Settings
Sometimes, the issue isn’t hardware failure but simply pushing the visual settings too high for your system’s capabilities. Unnecessarily high resolutions, extreme anti-aliasing, or complex shadow/lighting effects can cripple even powerful PCs.
Effective Troubleshooting and Fixes
1. Update Your Drivers (Crucial!)
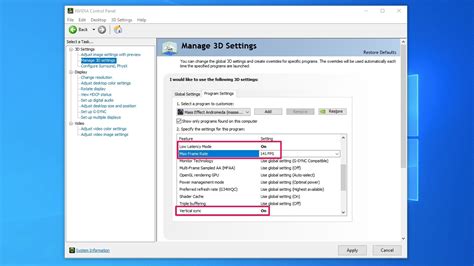
- Graphics Drivers: Always download the latest drivers directly from NVIDIA (GeForce Experience) or AMD (Radeon Software). Perform a “clean installation” if the option is available to remove old driver files.
- Chipset Drivers: Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website (or AMD/Intel directly) to ensure your chipset drivers are up to date.
- Windows Updates: Ensure your operating system is fully updated, as these often include performance enhancements and bug fixes.
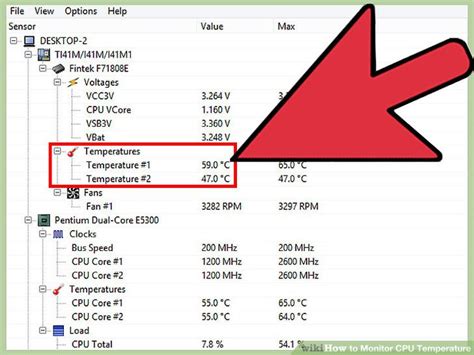
2. Monitor Temperatures
Use monitoring software like HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or NZXT CAM to keep an eye on your CPU and GPU temperatures while gaming. If temperatures consistently exceed 85-90°C (185-194°F), you might have an overheating issue. Consider:
- Cleaning dust from fans and heatsinks.
- Improving case airflow with additional fans.
- Replacing thermal paste on your CPU/GPU (advanced users).
- Investing in a better cooler.
3. Adjust In-Game Settings
Experiment with settings. Start by reducing the most demanding options:
- Resolution: Lowering this has a massive impact.
- Texture Quality: High settings demand more VRAM.
- Shadows and Lighting: These are often CPU and GPU intensive.
- Anti-Aliasing: Can be very demanding; try less intensive options or turn it off.
- V-Sync/G-Sync/FreeSync: Ensure these are correctly configured or try disabling V-Sync to see if it reduces input lag/stutter (though it may introduce screen tearing).
4. Optimize Background Processes
Before launching a demanding game:
- Close unnecessary applications (browsers, Discord, Spotify).
- Check Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) for high CPU/RAM usage from background processes. End tasks that aren’t critical.
- Disable startup programs you don’t need immediately via Task Manager’s “Startup” tab.
- Consider disabling Game Bar or other Windows gaming overlays if they cause issues.

5. Verify Hardware Compatibility and Upgrade (If Necessary)
Check the game’s minimum and recommended system requirements. If your hardware falls below the recommended specs, you might need to:
- Upgrade your GPU for better graphical performance.
- Increase RAM to at least 16GB (or 32GB for very demanding titles).
- Upgrade your CPU if it’s bottlenecking your GPU.
- Consider an SSD (NVMe is best) if you’re still on an HDD, as faster loading times and asset streaming can reduce stutter.
6. Power Management Settings
Ensure your Windows power plan is set to “High Performance” or “Ultimate Performance.” Sometimes, laptops or pre-built desktops default to balanced modes that limit performance. Also, check your GPU’s power management settings within its control panel (NVIDIA Control Panel or AMD Radeon Software) to ensure it’s set to “Prefer maximum performance.”
7. Scan for Malware and Viruses
Malicious software can consume system resources, leading to poor gaming performance. Run a full system scan with reputable antivirus software.

Conclusion
Diagnosing performance issues in new PC games can involve a bit of detective work, but by systematically checking your drivers, monitoring temperatures, optimizing settings, and ensuring your system’s health, you can often resolve most stuttering and low FPS problems. Remember that new games will always push hardware limits, and sometimes, a hardware upgrade is the ultimate solution to truly enjoy the latest titles at their best.