How to optimize GPU drivers for maximum gaming FPS and stability?

The Crucial Role of GPU Drivers in Gaming Performance
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) drivers are the essential software bridge between your operating system, games, and your graphics card. They dictate how efficiently your GPU renders graphics, directly impacting your gaming frame rates per second (FPS) and overall system stability. Unoptimized or outdated drivers can lead to performance bottlenecks, stuttering, visual artifacts, and even game crashes. Mastering the art of driver optimization is key for any serious PC gamer looking to extract every ounce of performance from their hardware.

Maintaining Optimal Drivers: Updates and Clean Installs
Staying Up-to-Date (But Smartly)
The first step in optimization is ensuring your drivers are current. NVIDIA and AMD regularly release new drivers that often include performance enhancements for the latest games, bug fixes, and general stability improvements. You can download these directly from their official websites or through their respective software (NVIDIA GeForce Experience, AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin Edition).
- NVIDIA: Use GeForce Experience for automatic updates or download directly from NVIDIA’s driver page.
- AMD: Use AMD Radeon Software for automatic updates or download directly from AMD’s support page.
While staying updated is good, immediately installing every new driver isn’t always best. Sometimes, a new driver might introduce unforeseen issues. It’s often wise to check community feedback before upgrading, especially for mission-critical setups.
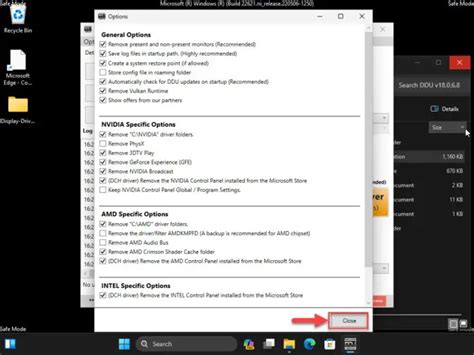
The Power of a Clean Installation with DDU
Over time, driver installations can leave behind remnants of old files, potentially leading to conflicts and performance issues. A ‘clean installation’ removes all previous driver components before installing new ones. For the most thorough clean install, a tool called Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) is highly recommended.
- Download DDU from its official source (Wagnardsoft).
- Boot your PC into Safe Mode.
- Run DDU, select your GPU vendor, and choose “Clean and restart.”
- Once restarted, install the latest GPU drivers.
This process ensures a fresh slate, minimizing the chances of driver conflicts hindering your performance or stability.
Deep Dive into Driver Control Panel Settings
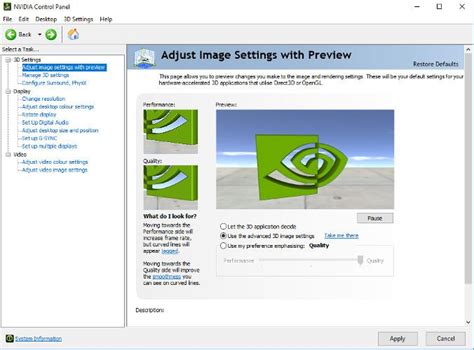
NVIDIA Control Panel Essentials
Access the NVIDIA Control Panel by right-clicking on your desktop. Here are critical settings for gaming performance:
- Manage 3D Settings > Global Settings:
- Power Management Mode: Set to “Prefer maximum performance” to ensure your GPU always runs at full clock speed when under load, preventing downclocking that can cause stuttering.
- Texture filtering – Quality: Change to “High performance.” This prioritizes FPS over subtle texture detail, which is often imperceptible during gameplay.
- Low Latency Mode: Experiment with “On” or “Ultra.” “Ultra” provides the lowest latency by submitting frames just-in-time for the GPU, but it can sometimes impact FPS on older hardware. Start with “On.”
- Shader Cache Size: Keep this on “Driver Default” or set to a higher value (e.g., 100 GB) for systems with ample storage. This stores compiled shaders to reduce stuttering.
- Anisotropic filtering: Generally best to control this in-game. If forced, “Application-controlled” is usually sufficient.
- Set PhysX Configuration: Ensure your GPU is selected for PhysX processing, not your CPU, if your card supports it.
AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin Settings
Open AMD Radeon Software by right-clicking on your desktop. Go to the “Gaming” tab for global and game-specific settings:
- Graphics Profile: Start with “Gaming” or “eSports” presets.
- Radeon Anti-Lag: Enable this to reduce input lag, similar to NVIDIA’s Low Latency Mode.
- Radeon Boost: Can dynamically lower resolution during fast-motion scenes to boost FPS, which might be useful for competitive gaming but can degrade image quality. Enable with caution.
- Image Sharpening: Can enhance visual clarity but might slightly impact performance. Adjust to your preference.
- Texture Filtering Quality: Set to “Performance” for maximum FPS.
- Enhanced Sync: An alternative to V-Sync that aims to reduce input lag while minimizing screen tearing when FPS exceeds refresh rate.
- Shader Cache: Ensure this is enabled.
Synchronizing Display and Game Settings
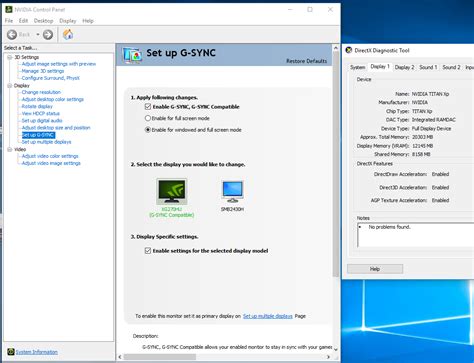
V-Sync, G-Sync, and FreeSync
Display synchronization technologies are vital for smooth gameplay. Screen tearing occurs when your GPU renders frames faster or slower than your monitor’s refresh rate. V-Sync locks your FPS to your monitor’s refresh rate, eliminating tearing but introducing input lag. Adaptive sync technologies (NVIDIA G-Sync and AMD FreeSync) are superior, dynamically adjusting your monitor’s refresh rate to match your GPU’s FPS, providing tear-free, low-latency gameplay. If you have a compatible monitor, ensure these are enabled in your driver settings and monitor OSD.
Game-Specific Profiles
Both NVIDIA and AMD allow you to create specific profiles for individual games. This is incredibly useful as some games might benefit from different settings than others. For example, a competitive shooter might prioritize low latency and high FPS, while a single-player RPG might benefit from higher texture quality and anti-aliasing. Always check the official game settings guides or community recommendations for optimal configurations.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting for Stability
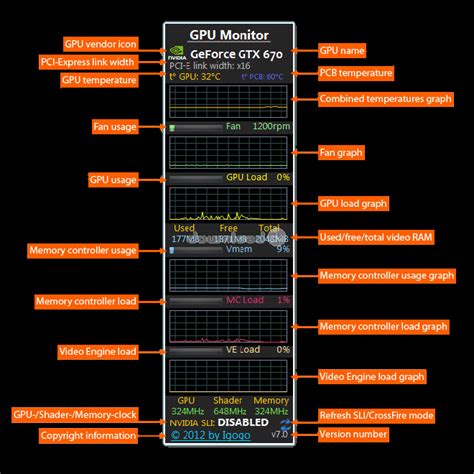
Monitoring Tools and Overlays
To verify the impact of your driver optimizations, use monitoring tools. MSI Afterburner (works with both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs) is excellent for monitoring FPS, GPU usage, temperature, and clock speeds. RivaTuner Statistics Server (RTSS), often bundled with Afterburner, provides a customizable in-game overlay. This helps you identify bottlenecks and confirm if your changes are yielding the desired results.
Driver Rollback and Stability
If a new driver causes instability, crashes, or performance degradation, don’t hesitate to roll back to a previous, stable version. You can do this via Windows Device Manager (right-click Start > Device Manager > Display adapters > [Your GPU] > Driver tab > Roll Back Driver). If that option is unavailable, use DDU to cleanly uninstall the problematic driver and then install an older, known-stable version from your GPU manufacturer’s website.
Conclusion
Optimizing your GPU drivers is a continuous process that involves staying updated, performing clean installations, and meticulously configuring settings within your driver control panel. By understanding the impact of each setting and tailoring them to your hardware and specific games, you can significantly boost your gaming FPS, eliminate stuttering, and ensure a stable, enjoyable gaming experience. Regular monitoring and a willingness to troubleshoot will keep your system running at its peak efficiency, delivering maximum performance and stability for all your gaming adventures.








