Gaming PC overheating: Best tips for airflow & preventing thermal throttling?

Why Your Gaming PC Overheats and What Thermal Throttling Means
An overheating gaming PC isn’t just a minor annoyance; it can severely impact performance, reduce component lifespan, and even lead to system instability. When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, it initiates a self-preservation mechanism called thermal throttling. This means your components automatically reduce their clock speeds and power consumption to lower temperatures, resulting in noticeable frame rate drops, stuttering, and an overall sluggish gaming experience.
Understanding the root causes – often poor airflow, accumulated dust, or inadequate cooling solutions – is the first step towards a cooler, more stable system. Ignoring these signs can lead to premature hardware failure, making preventative measures crucial for any serious gamer.

Optimizing Case Airflow: The Foundation of Good Cooling
Effective airflow is the backbone of any cool-running PC. It’s about moving cool air in and hot air out efficiently. Here’s how to master it:
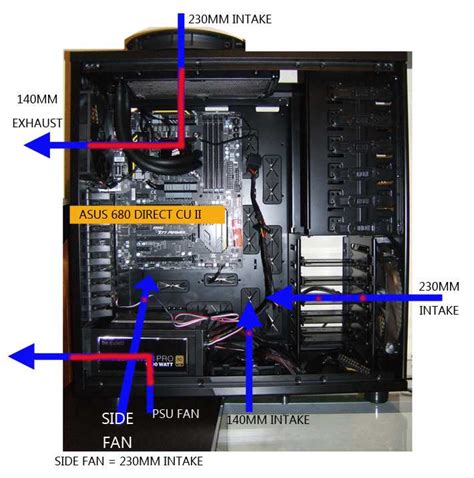
1. Strategic Fan Placement and Orientation
- Intake Fans: Position fans at the front and bottom of your case to draw cool air in. For optimal effect, these should be high-airflow fans.
- Exhaust Fans: Place fans at the rear and top of your case to push hot air out. Consider static pressure fans if they are blowing through a radiator or dense filter.
- Positive vs. Negative Pressure: Aim for slightly positive pressure (more intake than exhaust) to minimize dust ingress, as air will naturally leak out of unfiltered openings.
2. Cable Management is Key
Cluttered cables obstruct airflow, creating dead zones where heat can build up. Take the time to route cables neatly behind the motherboard tray and through designated cutouts. Use zip ties or Velcro straps to keep them tidy and out of the path of air movement.
3. Choose the Right Case
Not all PC cases are created equal. Look for cases designed with good airflow in mind, often featuring mesh front panels, multiple fan mounting options, and ample space for larger coolers.
Preventing Dust Buildup: Your PC’s Silent Killer
Dust is a thermal insulator and accumulates rapidly inside a PC, coating heatsinks, fans, and vents. This severely hinders heat dissipation.
- Regular Cleaning: Establish a cleaning routine every 3-6 months. Use compressed air to blow dust out of heatsinks (CPU, GPU), power supply, and case fans. Hold fans steady while cleaning to prevent over-spinning.
- Dust Filters: Ensure your case has filters on all intake vents. Clean these filters frequently (monthly or more) to maintain proper airflow.

Upgrading Cooling Components for Maximum Performance
Sometimes, stock coolers just aren’t enough, especially for powerful gaming hardware.
1. CPU Cooler Upgrade
- Air Coolers: High-performance air coolers with large heatsinks and multiple heat pipes are often quieter and just as effective as entry-level liquid coolers.
- All-in-One (AIO) Liquid Coolers: Offer excellent cooling performance, especially for overclocked CPUs. Ensure your case can accommodate the radiator size (e.g., 240mm, 360mm).
2. GPU Cooling Solutions
While most GPUs come with competent coolers, severe throttling might require intervention:
- Custom Fan Curves: Use software (like MSI Afterburner) to create a more aggressive fan curve, increasing fan speeds earlier than the default settings.
- Undervolting: Reduce your GPU’s voltage slightly while maintaining performance. This lowers power consumption and heat output without significant performance loss.

Thermal Paste: The Critical Interface
The thermal paste between your CPU/GPU and their respective heatsinks facilitates heat transfer. Over time, it can dry out and become less effective.
- Reapplication: If your CPU/GPU temperatures are unusually high despite good airflow, consider reapplying high-quality thermal paste. This involves carefully cleaning off the old paste and applying a fresh, thin layer.
- Application Method: A pea-sized dot or a single line in the center of the CPU/GPU die is generally recommended, allowing the pressure from the heatsink to spread it evenly.
Monitoring and Testing Your System
Knowledge is power. Regularly monitor your PC’s temperatures to catch issues before they become critical. Use software tools like HWMonitor, HWiNFO, or your motherboard’s utility to track CPU and GPU temperatures while gaming or under load. Stress tests can also help identify thermal weaknesses.
Conclusion: A Cooler PC for Better Gaming
Preventing your gaming PC from overheating and throttling is an ongoing process that combines smart setup, regular maintenance, and occasional upgrades. By focusing on optimized airflow, diligent dust control, and ensuring adequate cooling for your core components, you’ll not only enjoy smoother, more consistent performance but also extend the life of your valuable hardware. A cool PC is a happy PC, and a happy PC makes for a happy gamer.








