My gaming PC overheats. How can I improve airflow & cooling effectively?

Understanding PC Overheating and Its Impact
An overheating gaming PC isn’t just an annoyance; it’s a serious threat to your system’s longevity and performance. High temperatures can lead to thermal throttling, where your CPU and GPU automatically reduce their clock speeds to prevent damage, resulting in lower frame rates and stuttering gameplay. Prolonged exposure to excessive heat can also shorten the lifespan of crucial components, leading to costly replacements. Addressing overheating proactively is essential for a stable, high-performance gaming experience.
Diagnosing Overheating: What to Look For
Before you can fix an overheating issue, you need to confirm it’s actually happening and identify which components are running hot. Common signs include unusually loud fan noise, sudden system crashes or reboots, performance drops during gaming, and a hot-to-the-touch PC case. To accurately diagnose, use monitoring software like HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or NZXT CAM to check CPU, GPU, and even motherboard temperatures while gaming or under heavy load.
Typical safe operating temperatures for a CPU under load are generally below 80°C (176°F), while GPUs can often run a bit hotter, sometimes up to 85°C (185°F) or even 90°C (194°F) for certain models. If your components are consistently exceeding these thresholds, it’s time to take action.

Immediate & Essential Steps for Better Airflow
1. Clean Your PC Thoroughly
Dust is the number one enemy of PC cooling. Over time, it accumulates on fan blades, heatsinks, and vents, creating an insulating layer that traps heat and obstructs airflow. Regularly (every 3-6 months) clean your PC using compressed air. Disconnect the power, take your PC outside or to a well-ventilated area, and use short bursts of air to dislodge dust from heatsinks (CPU, GPU), fan blades, and all intake/exhaust vents. Hold fan blades gently to prevent them from spinning too fast, which can damage their bearings.

2. Optimize Cable Management
Messy cables inside your PC case can act as barriers, disrupting the smooth flow of air. Spend some time routing your cables neatly behind the motherboard tray or bundling them discreetly away from direct airflow paths. This seemingly small detail can significantly improve internal air circulation.
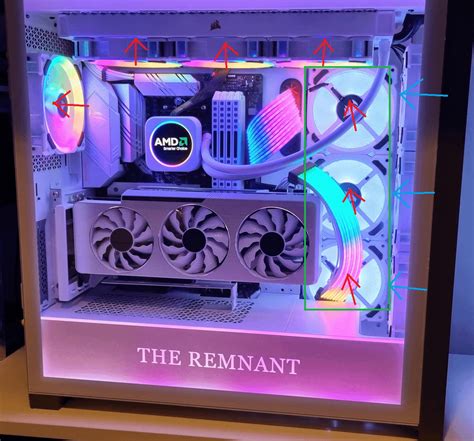
3. Improve Case Fan Configuration
The number, size, and orientation of your case fans play a critical role in establishing effective airflow. The goal is to create a clear intake-to-exhaust path:
- Intake Fans: Typically mounted at the front and bottom of the case, pulling cool air in.
- Exhaust Fans: Usually located at the rear and top, pushing hot air out.
Aim for a slightly positive air pressure setup (more air coming in than going out) to help prevent dust from settling in unfiltered areas. Ensure your fans are pushing air in the correct direction – there’s usually an arrow on the side of the fan indicating airflow direction.

4. Ensure Proper Case Selection
If your PC case has poor airflow by design (e.g., solid front panel with minimal vents), it might be a significant bottleneck. Modern cases often feature mesh front panels and ample space for multiple fans to maximize airflow. If your current case is restrictive, consider upgrading to one known for its excellent thermal performance.
Advanced Cooling Solutions & Upgrades
1. Reapply Thermal Paste
The thermal paste between your CPU (or GPU) and its heatsink degrades over time, becoming less effective at transferring heat. If your CPU or GPU temperatures are high despite clean fans and good airflow, reapplying fresh thermal paste can make a dramatic difference. This requires carefully removing the cooler, cleaning off old paste with isopropyl alcohol, and applying a small amount of new, high-quality paste.
2. Upgrade CPU Cooler
Stock CPU coolers are often adequate for general use but can struggle with the heat generated by modern gaming CPUs under load. Upgrading to a more powerful aftermarket air cooler (with larger heatsinks and fans) or an All-In-One (AIO) liquid cooler can significantly lower CPU temperatures. AIOs use a pump, radiator, and fans to dissipate heat more efficiently.

3. Consider GPU Cooling Solutions
While often more complex, if your GPU is consistently overheating, you can explore options like custom fan curves, undervolting the GPU (reducing its power consumption while maintaining performance), or, for advanced users, considering an aftermarket GPU cooler or a custom liquid cooling loop.
Beyond Hardware: Software & Environment
1. Monitor and Adjust Fan Curves
Many motherboards and GPUs allow you to set custom fan curves in the BIOS/UEFI or through software utilities. This lets you control how aggressively your fans spin based on component temperatures. A well-tuned fan curve can provide a better balance between cooling performance and noise levels.
2. Optimize Room Environment
The ambient temperature of your room also plays a role. Keep your PC in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Ensure there’s enough space around the PC case for air to circulate freely.
Conclusion
Improving airflow and cooling in your gaming PC is a multi-faceted approach. By combining regular maintenance, strategic hardware adjustments, and smart software settings, you can effectively combat overheating, ensure your components run at optimal temperatures, and enjoy a smoother, more reliable gaming experience for years to come. Remember, consistent monitoring is key to catching potential issues before they become serious problems.








