My PC lags in new games. How do I diagnose performance bottlenecks?

Modern games demand significant processing power, and it’s frustrating when your otherwise capable PC struggles to keep up. Experiencing lag, stuttering, or low frame rates in new titles often points to a performance bottleneck – a single component limiting the overall system’s potential. Diagnosing this issue systematically is key to resolving it and getting back to smooth gaming.
What is a Performance Bottleneck?
In simple terms, a performance bottleneck occurs when one component in your system is significantly slower or less capable than the others, thereby limiting the maximum performance of the entire system. Think of it like a highway with many lanes suddenly narrowing to just one; traffic can only flow as fast as that single lane allows. For gaming PCs, common culprits include the CPU, GPU, RAM, or even your storage drive.
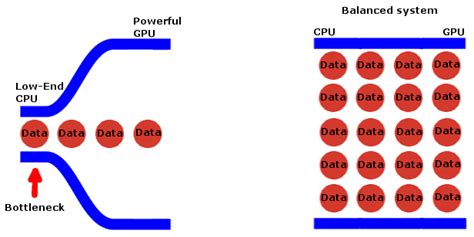
Step 1: Initial Checks and Software Preparation
Update Your Drivers
Outdated graphics drivers are a frequent cause of poor game performance. Always ensure your GPU drivers (NVIDIA GeForce Experience, AMD Radeon Software) and chipset drivers are up to date. This can often provide significant performance boosts and stability improvements.
Monitor Performance In-Game
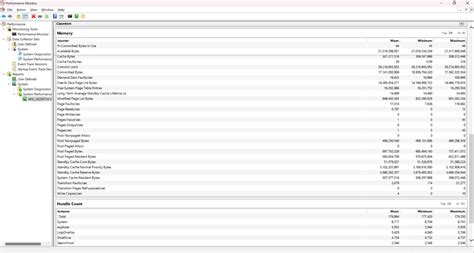
To accurately diagnose bottlenecks, you’ll need performance monitoring software. Tools like MSI Afterburner (with RivaTuner Statistics Server), HWiNFO, or even Windows Task Manager can display real-time usage statistics for your CPU, GPU, RAM, and VRAM while you play. Configure these tools to show an on-screen overlay during gameplay.

Step 2: Analyzing Key Components During Gameplay
Launch a new, demanding game that exhibits the lagging issue. Play for a few minutes while closely observing the usage percentages of your core components.
Graphics Card (GPU)
If your GPU usage consistently hovers around 95-100% and your frame rates are still low, it’s a strong indicator that your GPU is the primary bottleneck. It means the graphics card is working at its maximum capacity and cannot render frames any faster. Also check VRAM usage; if it’s consistently at or near its limit, that can also cause stuttering.
Processor (CPU)
If your CPU usage is consistently high (e.g., above 90% on multiple cores, or near 100% on a few core threads) while your GPU usage is relatively low (e.g., 60-70% or less), then your CPU is likely the bottleneck. The CPU can’t feed the GPU data fast enough, leaving the GPU underutilized. Check individual core usage, as some older games might not utilize all cores effectively.

System Memory (RAM)
Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and go to the “Performance” tab, then select “Memory.” If your RAM usage is consistently very high (e.g., 90% or more) and you notice frequent disk activity even without specific game loading, you might be running out of RAM. This forces the system to use your storage drive as virtual memory, which is significantly slower and causes stuttering.
Storage Drive (SSD/HDD)
While less common as a direct cause of in-game lag, a slow storage drive can lead to extremely long loading times and texture pop-in. If your game is installed on an older HDD, upgrading to an SSD (Solid State Drive) can drastically improve load times and overall responsiveness. Monitor disk usage in Task Manager during loading screens or when new assets are streaming in.
Step 3: Interpreting the Data and Next Steps
- GPU Bottleneck: Your graphics card is struggling. Consider lowering graphics settings (resolution, texture quality, anti-aliasing) or upgrading your GPU.
- CPU Bottleneck: Your processor can’t keep up. Lower CPU-intensive settings like crowd density, draw distance, or physics calculations. An upgrade to a newer, faster CPU might be necessary, potentially requiring a new motherboard and RAM.
- RAM Bottleneck: You need more RAM. Adding more RAM (e.g., upgrading from 8GB to 16GB, or 16GB to 32GB) or ensuring your existing RAM is running in dual-channel mode at its advertised speed can help.
- Storage Bottleneck: Upgrade your game installation drive to an SSD. This won’t boost FPS directly but will significantly improve loading times and potentially reduce stuttering caused by asset streaming.

By systematically monitoring your PC’s performance and understanding what each component’s usage indicates, you can accurately pinpoint the bottleneck. This precise diagnosis empowers you to make informed decisions about optimizing settings or upgrading hardware, ensuring a smoother and more enjoyable gaming experience with new titles.








