Optimizing game settings for max FPS on a mid-range gaming PC?
Unlocking Peak Performance on Your Mid-Range Rig
Owning a mid-range gaming PC means balancing visual fidelity with performance. While you might not be pushing 4K at 144 FPS, you can absolutely optimize your setup to achieve a consistently smooth and enjoyable experience, often hitting that coveted 60+ FPS mark. The key lies in understanding which settings impact performance most and how to fine-tune them.
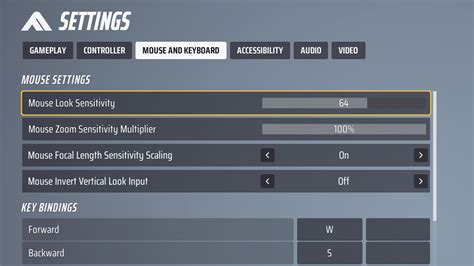
Prioritizing In-Game Graphics Settings
Most of your FPS gains will come from strategically adjusting settings within the game itself. Not all settings are created equal; some have a disproportionately high impact on performance.
- Resolution: Always aim for your monitor’s native resolution. If FPS is still low, try scaling down the render resolution (if available) within the game before changing the overall display resolution.
- Render Scale: This is arguably the most impactful setting. Reducing it to 80-90% can provide significant FPS boosts with only a slight visual downgrade. Conversely, setting it above 100% is like playing at a higher resolution, costing massive FPS.
- Shadows: Shadows are notoriously demanding. Lowering shadow quality, resolution, or even disabling them entirely (if acceptable visually) can free up a lot of frames.
- Anti-Aliasing (AA): While essential for smoothing jagged edges, AA methods like MSAA are very resource-intensive. Try less demanding options like FXAA or TAA, or even disable it if you have a high-resolution monitor where jaggies are less noticeable.
- Post-Processing Effects: Settings like Ambient Occlusion, Volumetric Fog, Screen Space Reflections, and Motion Blur can be huge FPS killers. Reduce or disable them first.
- Texture Quality: This mainly depends on your GPU’s VRAM. If you have 6GB or more, you can often keep textures on High. If you have 4GB or less, dropping them to Medium or Low will prevent VRAM bottlenecks.
- Draw Distance / View Distance: This affects how far away objects and details are rendered. Lowering it can help, especially in open-world games, but it might reduce immersion.
- V-Sync: Disable V-Sync for maximum FPS, as it caps your frame rate to your monitor’s refresh rate and can introduce input lag. Use an in-game FPS limiter or a GPU driver one instead.
System-Level Optimizations for Gaming
Beyond in-game settings, your operating system and drivers play a crucial role in overall performance.
- Update Your Drivers: This is paramount. Always keep your GPU drivers (NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Radeon Software) updated to the latest stable version. Also, ensure your chipset drivers and Windows are up to date.
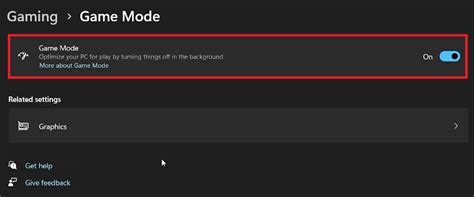
- Windows Game Mode: Ensure Windows Game Mode is enabled. It prioritizes your game’s resources and suppresses background tasks.
- Power Plan: Set your Windows power plan to “High Performance” (or “Ultimate Performance” if available) under Power Options.
- Close Background Applications: Any application running in the background (browsers, Discord, Spotify, etc.) consumes CPU, RAM, and GPU resources. Close unnecessary apps before launching a game.
- Disable Startup Programs: Use Task Manager to disable non-essential programs from launching with Windows.
- Disk Space & Defragmentation: Ensure your gaming drive isn’t full. If you’re on an HDD, consider defragmenting it (though not for SSDs).
Fine-Tuning with GPU Software
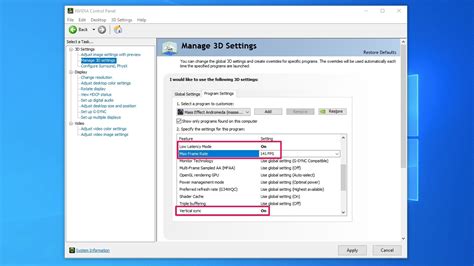
NVIDIA and AMD provide robust control panels that allow for global and game-specific optimizations.
- NVIDIA Control Panel / AMD Radeon Software: Explore these settings for options like “Low Latency Mode” (NVIDIA) or “Radeon Anti-Lag” (AMD) to reduce input delay.
- Image Scaling/Upscaling: Utilize NVIDIA DLSS, AMD FSR, or Intel XeSS if your game and GPU support them. These technologies render the game at a lower resolution and then intelligently upscale it, offering significant FPS boosts with minimal visual loss. Even if the game doesn’t support it directly, NVIDIA’s Image Scaling and AMD’s Radeon Super Resolution can be enabled globally.
- Texture Filtering Quality: Set this to “High Performance” in your GPU control panel.
- Power Management Mode (NVIDIA): Set to “Prefer Maximum Performance.”
![NVIDIA Control Panel [Download & Install Guide]](/images/aHR0cHM6Ly90czEubW0uYmluZy5uZXQvdGg/aWQ9T0lQLmNsVFFJRjVIODRKVE83d0VUN0szRndIYUU4JnBpZD0xNS4x.webp)
Monitoring and Iteration is Key
Optimization is an ongoing process of trial and error. Use an FPS counter (like the one built into Steam, GeForce Experience, Radeon Software, or MSI Afterburner) to monitor your frame rate in real-time. Make one change at a time, test its impact, and then decide if the visual trade-off is worth the FPS gain.
Start by making the most impactful changes first (render scale, shadows, post-processing), then move on to finer adjustments. Every game engine is different, and what works best in one title might not be optimal in another.
Conclusion
Achieving maximum FPS on a mid-range gaming PC is entirely feasible with a systematic approach. By carefully adjusting in-game graphics, optimizing your operating system, and leveraging your GPU’s software, you can significantly enhance your gaming experience. Remember, the goal isn’t just raw numbers, but a smooth, responsive, and enjoyable gameplay session. Experiment, monitor, and find the perfect balance that works for your specific hardware and your favorite titles.